[ad_1]
Background
From time immemorial Nepali households have had at the least one member away from house for work or schooling, depicting a sample of migration within the nation. The variety of outmigrants as per the Division of Overseas Employment (DoFE) in Nepal was solely 3,605 in 1993/94, which has now elevated to over 5 million as of 2019/20 revealed within the Nepal Migration Report 2020 by the Ministry of Labour, Employment and Social Safety (MOLESS). Nevertheless, labor migration in Nepal has principally remained a male phenomenon as the feminine migrant staff accounted for a bit of greater than 5% within the final decade. Given such a scenario, it’s crucial to delve into the tendencies of feminine labor migration in Nepal, its causes and patterns over these years.
Feminine labor migration in Nepal and its causes
Though there have been rigorous research associated to migration processes and their results on the economic system, comparatively much less consideration has been given to feminine migrants in Nepal. Nonetheless, the migration of Nepali girls is an previous narrative and one of many main components for that is considered feminization of poverty. To place it extra merely, feminization of poverty was recognized as a significant component contributing to Nepali girls looking for international employment in a research carried out by the Asia-Pacific Analysis and Coaching Community on Commerce (ARTNeT). As per the research, girls’s home care companies are in plentiful provide and require minimal financial funding, pushing them emigrate as a hedge in opposition to poverty. To validate this assertion, the Worldwide Labor Migration report states that an estimated 67 million home staff worldwide exist the place 80% are girls and ladies who carry out such work both paid or unpaid. At the moment, globalization has additionally made this a straightforward selection for such girls.
Apart from, such a bent in feminine migration is especially frequent in underdeveloped and creating nations the place girls migrate to help the care economic system of the developed nations. It is because it’s believed that ladies from creating nations have the familiarity with home care expertise on account of their gender roles. Furthermore, globally, additionally it is conceptualized that care companies are merchandise that may be purchased and bought available in the market. Given this, most underdeveloped and creating nations, together with Nepal, have seen a rise in feminization of labor migration.
Moreover, most literature within the case of Nepal opine that feminine migrant transfer majorly due to the shortage of financial prospects and poor residing situations. Male members of Nepali households are usually supplied with formal schooling and expertise coaching. After marriage, both the male members or older girls of the household make selections about purchases, every day bills, and shopping for or promoting belongings, limiting newly-wed females’ authority. In consequence, girls are obliged to juggle home duties with different obligations like farming. There are additionally extra push components for girls to hunt employment overseas, equivalent to marital points, gender discrimination, bettering kids’s future, and servicing money owed at house. This means that the choice emigrate amongst most feminine migrants is influenced by family financial issues.
Furthermore, feminine migrants with a better stage of mobility previous to migration, equivalent to work of membership in group teams, are extra assured in migrating abroad for profession alternatives. Ladies can even escape repressive societal traditions and stigmas by migrating, and that is principally for divorced, widowed or separated girls.
As well as, the Nationwide Residing Requirements Survey 2010/11 carried out by the Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) presents findings on the absentee feminine inhabitants. Below this, when it comes to proportion, extra girls than males traveled to pursue schooling. Nevertheless, the relocation for females is sure by difficulties ranging from their houses/households, their nation, to the nation of transit, and the nation of employment. Nonetheless, all of those components encourage girls emigrate overseas.
Patterns of feminine migration in Nepal
The sample for feminine migrant staff differs barely and reveals a larger selection than for male migrants. Owing to the open border that Nepal shares with India and its shut socio-cultural ties, India has been probably the most most popular labor vacation spot for Nepalis. Traditionally, feminine migration from Nepal was linked to cross-border marriages in India, resettlement of whole households in Northeast India, Burma, and Bhutan, or being lured/trafficked into working as intercourse staff. Whereas such a sample of migration to India remains to be frequent and principally undocumented, many ladies additionally began migrating independently for employment in international locations.
In Nineteen Eighties, Nepali girls started to journey to Southeast and East Asia. After the Folks’s motion of 1990 in Nepal, feminine migration as worldwide laborers, primarily home staff and caregivers, picked up. By the Nineteen Nineties, their migration was concentrated within the home and repair sectors in Hong Kong and Japan. Within the 2000s, nations within the Arab States started attracting extra Nepali feminine migrants to work as home and repair staff. By 2007, an estimated 80% of Nepali girls working within the Arab States have been enterprise home work inside non-public households, equivalent to cleansing, cooking, or caring for kids or aged members of the family. Different Nepali girls migrants labored in inns, eating places, catering, manufacturing, medical companies and wonder parlors each inside Asia and overseas.
In more moderen occasions, UAE, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Cyprus are the highest 5 nations the place 77% of whole feminine migrants of Nepal go for employment. Furthermore, over 50% of Nepali feminine migrants hail from districts of Provinces 1 and three equivalent to Jhapa, Sindhupalchok, Makwanpur, Morang, Kathmandu, Kavrepalanchok, Ilam, Nuwakot, Sunsari, and Chitwan. This information is constant in 2017/18 and 2018/19 as per the most recent report.
Pattern in feminine labor migration in Nepal
Feminine migration was undocumented and unlawful until 2007 within the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) and different neighboring nations. As per the DoFE, greater than 176,000 girls have obtained labor permits since 2008 to go to labor locations such because the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Kuwait, Malaysia, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Cyprus, and Jordan. Contrastingly, one other report by the DoFE acknowledged that solely 21,412 Nepali girls have been legally working abroad as of 2014/15. The variety of labor permits obtained by feminine migrants surged by 106% between 2010/11 and 2014/15 compared to a rise of solely 39% of male migrants. The share of feminine migrants stood at round 8.5% in 2018/19 as per the Nepal Labor Migration Report 2020.
The determine under exhibits the pattern within the variety of outmigrants by disaggregating the labor approvals by gender to point out the rise in feminine labor migration through the years:
Determine 1 Pattern in acquiring labor approvals (Disaggregated by gender when it comes to the entire quantity)
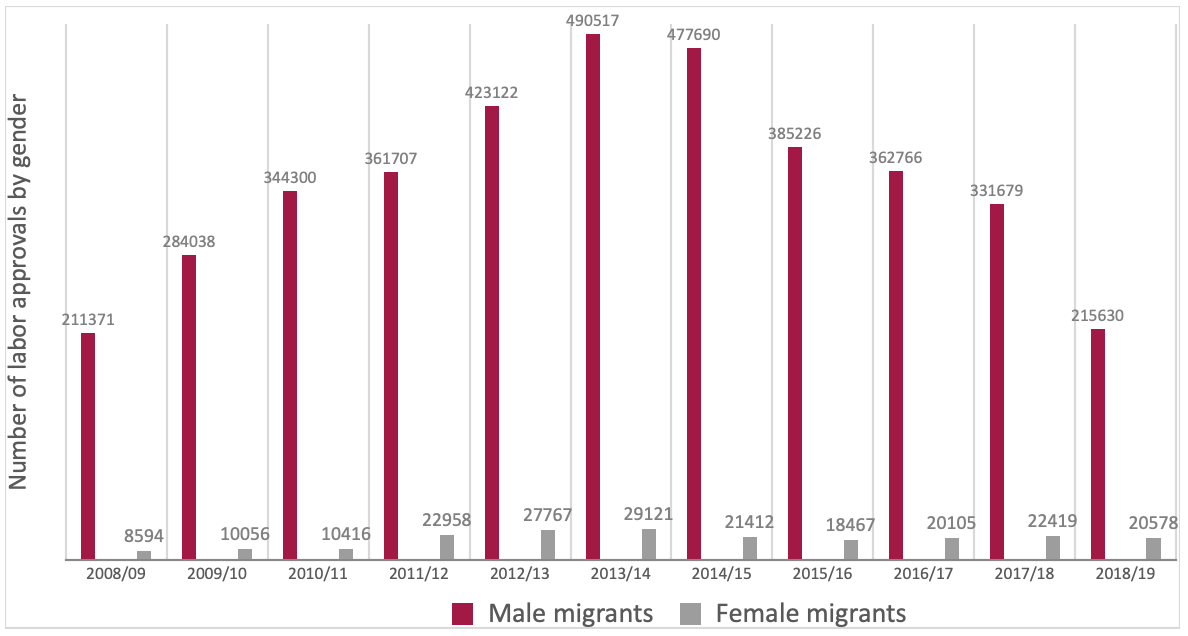
Supply: Nepal Labor Migration Report 2020
No matter the variety of migrants, the Worldwide Group for Migration (IOM) acknowledges that migration can reorganize gender relations and energy chains or hierarchies by permitting folks to enhance their financial well-being and help themselves and their deserted family members and members of the family. Though MOLESS states that migration in Nepal is a male phenomenon, feminine migration is, undoubtedly, on the rise. It has the potential to assist construct their lifestyle and the Nepali economic system given they’re additionally financial brokers of the nation contributing by way of remittances to the nation’s economic system.
[ad_2]
Source link


