[ad_1]
International direct funding is particularly necessary now for an import dependent Nepal with a widening commerce deficit, and declining overseas reserves. Making a facilitating setting for FDI is necessary to advertise and encourage manufacturing inside the nation..
International Direct Investments in Nepal are regulated primarily by the International Funding and Know-how Act (FITTA) of 2019, together with extra provisions relevant from the Public Personal Partnership and Funding Act, Labor Act, and the Corporations Act.
FITTA was first launched in 1992 and later revised in 2019. Underneath FITTA, the minimal threshold for overseas funding in Nepal is NPR 50 million. The FITTA 2019 permits corporations with overseas funding to borrow from overseas banks and monetary establishments if approval from Nepal Rastra Financial institution (NRB) and advice from involved ministry is obtained. The Act has additionally clarified on the present provisions of dividend repatriation, income, earnings, and proceeds that are topic to the approval of regulators. A 2021 revision to the FITTA requires overseas traders in Nepal to convey 70% of their proposed funding earlier than graduation of operations, and one other 30% inside the subsequent two years.
The Public Personal Partnership and Funding Act stipulates investments as much as NPR 6 billion to be authorized by the Division of Business, whereas investments above NPR 6 billion must be authorized by the Funding Board of Nepal. This act can also be relevant to overseas direct investments.
Standing of International Direct Funding in Nepal
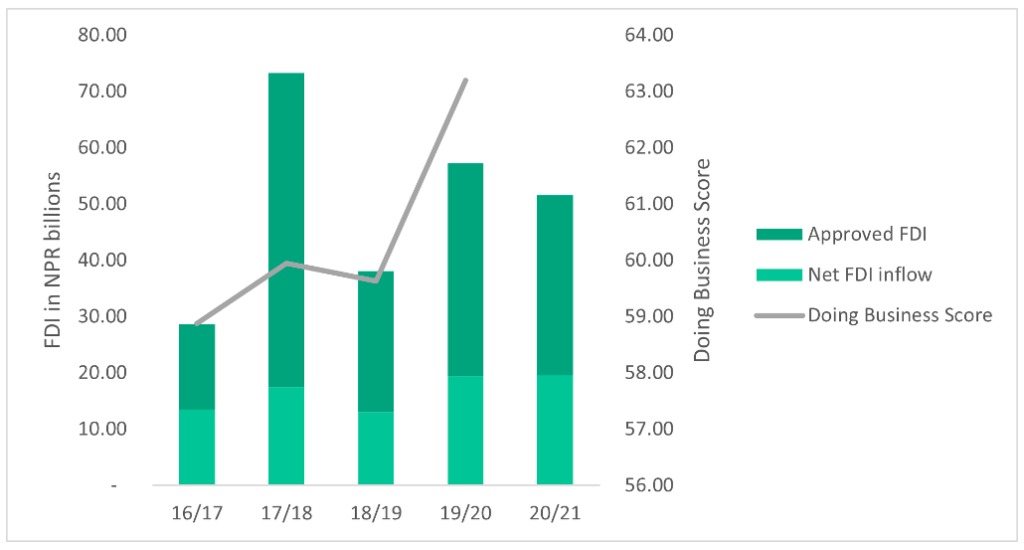
The authorized FDI represents an intent to speculate, however as seen in Determine 1, these investments don’t match the influx of FDI. Web FDI influx, complete influx of FDI minus repatriation, represents 57% of the authorized quantity on common in all 5 years. This discrepancy exists due to the numerous time lags between approval and precise funding.
The introduction of FITTA in 2019 elevated authorized FDI by 51.3% and web FDI influx by 49.2% within the fiscal yr 2019/20 in comparison with the earlier fiscal yr. Regardless of the authorized FDI is decrease at 2019/20 in comparison with 2017/18 by 32.2%, FDI influx elevated by 11.3% for a similar interval. The 2021 revision of FITTA, as talked about above, would possibly shut the hole between the authorized FDI and precise FDI influx within the nation.
The Doing Enterprise Index revealed yearly by the World Financial institution measures the benefit of doing enterprise in 190 nations in areas reminiscent of beginning a enterprise, entry to credit score and contract enforcement to call a number of. Nepal’s general rating within the index diminished by 1.53 factors in 2017, elevated by 1.07 factors in 2018, once more decreased by 0.32 in 2019, rising considerably in 2020 by 3.57 factors. The numerous enchancment in rating of 2020 could be attributed to the revision of FITTA and introduction of Public Personal Partnership and Funding Act and Particular Financial Zone Act in 2019.
Determine 1: Authorized FDI, Web FDI influx and Doing Enterprise Rating over 5 years (Supply: NRB and World Financial institution)
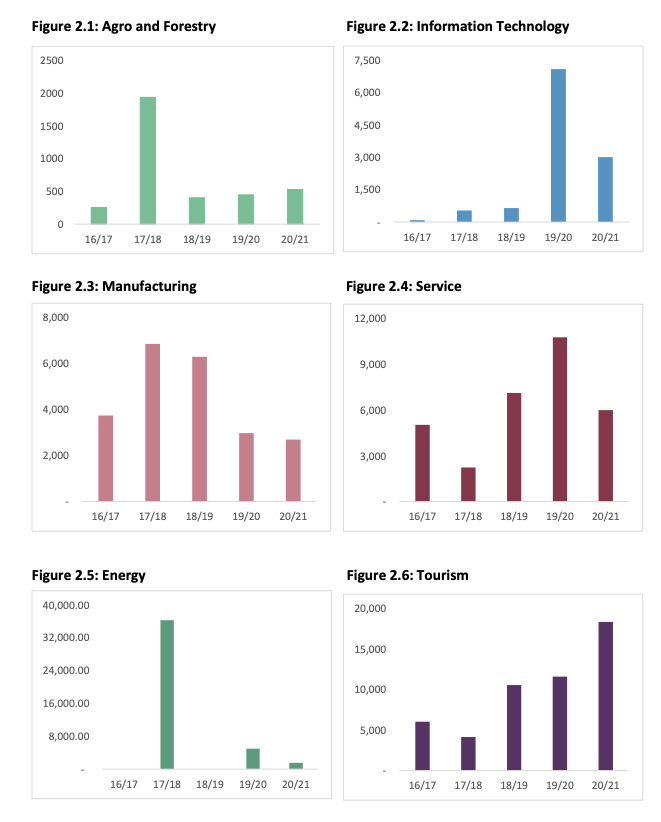
The Division of Business classifies FDI authorized by Nepal into Agro Forestry, Data Know-how, Manufacturing, Service, Power and Tourism. The Data Know-how sector has skilled the very best Compounded Common Progress Fee (CAGR) of 141.23% over a interval of 5 years, adopted by Tourism sector at 32.14%, Agro and Forestry sector at 19.84%, and the service sector at 4.5%. The manufacturing trade has skilled a unfavorable CAGR of seven.87%. Because the CAGR is a mean, the FDI in numerous sectors usually are not rising at a uniform price as seen in Determine 2. NPR 36.25 billion value of FDI was authorized within the vitality sector in 2017/18, which diminished to zero in 2018/19 and skilled a fall of 86.3% in 2019/20.
Determine 2: Authorized FDI by sector over 5 years (figures in NPR tens of millions) (Supply: Industrial Statistics, Division of Business)
Constraints in International Funding in Nepal
Whereas the introduction of FITTA has improved the setting for overseas direct funding in Nepal, among the many remaining constraints are explored under.
Prolonged approval course of: Approval of overseas direct funding is to be obtained from a number of authorities which makes the method pricey and time consuming. The Single Window System provisioned by the revised FITTA has not been totally applied. The registration of overseas corporations could be made on-line by means of the Workplace of Firm Registrar’s web site, nevertheless, extra bodily copies of paperwork are incessantly requested.
Limits on International Borrowings: A restrict of LIBOR + 5.5% is imposed on rates of interest that may be charged by overseas lenders to all sectors. This won’t adequately replicate the dangers related to sure sectors.
Additional, NRB doesn’t permit cost of overseas borrowings if there are excellent loans to overseas banks. This would possibly trigger hesitancy amongst overseas lenders as they understand lending to Nepal as a protentional danger. International lenders are unable to extend rates of interest to regulate for, such dangers as a result of rate of interest restrict. Thus, Nepal won’t obtain overseas funding within the type of debt.
Repatriation of income: Repatriation requires approval from a number of businesses reminiscent of Nepal Rastra Financial institution together with related authorities departments and in some instances, additionally division of trade. For investments within the telecommunications sector, approval from Nepal Telecommunications Authority is required, whereas the approval from the Ministry of Finance is required for investments in joint ventures.
Certification of revenue tax cost of royalties should be submitted to the Division of Business. The involvement of DoI in what must be the accountability of income assortment company causes pointless bottleneck for repatriation of FDI.
Although repatriation is low in comparison with the influx of FDI, the time-consuming approval requirement would possibly discourage overseas traders.
Lack of danger administration merchandise: Nepal lacks the danger administration merchandise required to hedge the rate of interest and overseas foreign money dangers related to overseas funding. This downside is particularly evident in massive hydropower and infrastructure tasks which receives overseas funding within the type of debt. The income of such tasks is denominated in NPR and debt reimbursement is to be made in overseas foreign money. Since Nepal Electrical energy Authority (NEA) has stopped signing Energy-Buy Settlement (PPA) in greenback denomination, an absence of hedging instrument for a depreciating Nepali Rupees has considerably decreased overseas funding within the vitality sector as seen in Determine 2. Attributable to an absence of settlement on hedging premium, the newly launched hedging regulation has failed to handle this downside.
Sub-par copyright legal guidelines: Nepal’s Copyright Act doesn’t meet the worldwide requirements of mental property rights. Model names and emblems of well-recognized manufacturers are consistently infringed upon by making slight modifications the letters, whereas sustaining the colour scheme or brand. A number of instances of trademark infringement by the Multinational Corporations (MNCs) have been filed, nevertheless, actions towards such instances are restricted. Nepal doesn’t acknowledge patents awarded by different nations. A low enforcement of copyright legal guidelines and safety of mental property rights discourages new MNCs to enter Nepal.
International direct funding is particularly necessary now for an import dependent Nepal with a widening commerce deficit, and declining overseas reserves. Making a facilitating setting for FDI is necessary to advertise and encourage manufacturing inside the nation. Stakeholder consultations are required to handle particular provisions within the laws which are constraining overseas funding. Nevertheless, merely selling FDI in conventional industries isn’t sufficient. A world that’s more and more impacted by local weather change, selling FDI in inexperienced and sustainable companies must be prioritized and mirrored in insurance policies.
[ad_2]
Source link


