[ad_1]
DUBAI: Dutch teachers and the UN’s Meals and Agriculture Group have launched an important new challenge that’s utilizing state-of-the-art synthetic intelligence expertise to enhance the identification and measurement of fish species and shares within the Nile Basin.
It may turn out to be a key software within the quest for sustainability and meals safety by enhancing the gathering of significant knowledge from fishing communities across the area.
The initiative, supported by Wageningen College and Analysis within the Netherlands, is the most recent improvement in a decades-long effort launched within the Seventies by FAO to assist nations perform higher identification of species for fisheries functions, in order that the gathering of knowledge about fish catches might be enhanced and the fishing business improved.
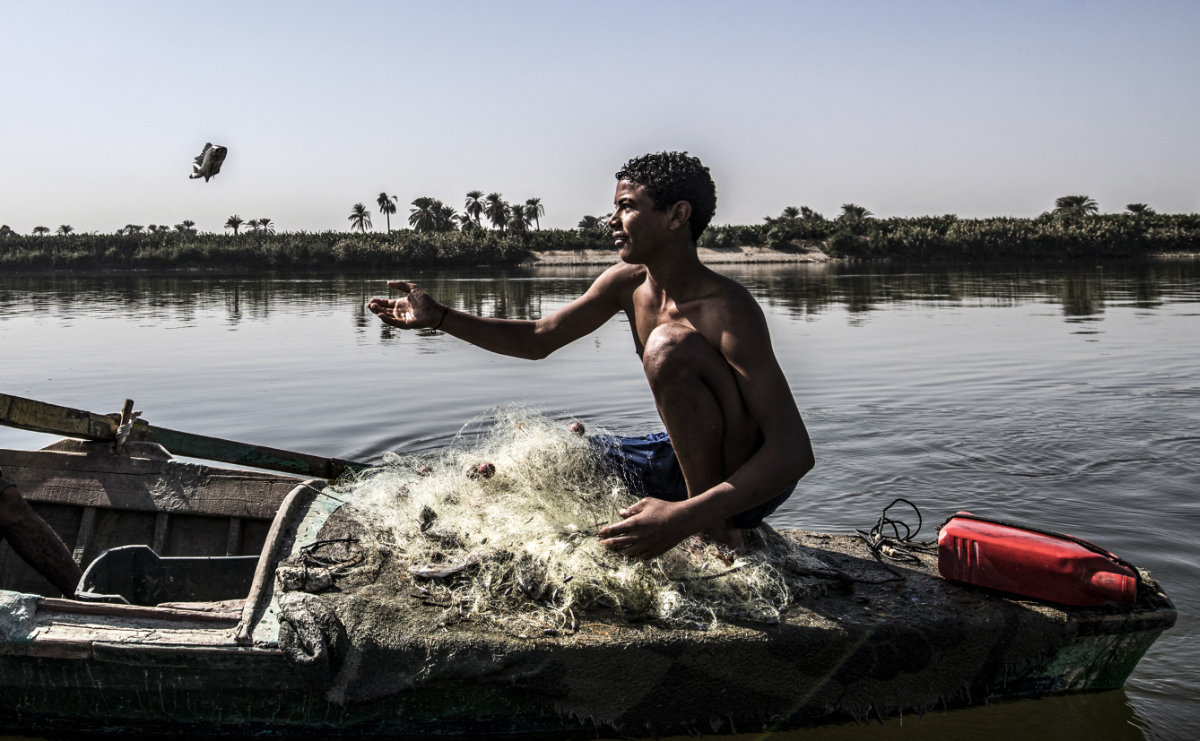

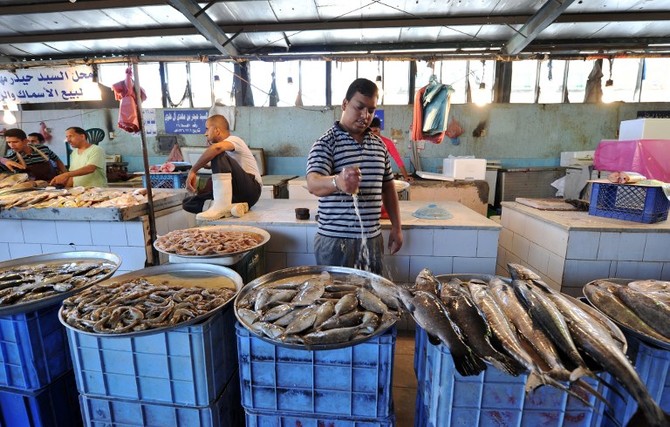
“This helps individuals to know long-term developments in what is occurring with fisheries by time,” mentioned Kim Friedman, a senior fishery sources officer at FAO. “The preliminary push was primarily to do species identification guides and most of those had been finished with the museums of the world, so {that a} nation may decide up a information and know precisely which species it was. However then we began to additionally do posters and pocket guides so individuals may carry them in boats.”
The instruments have advanced because of essential new work, supported by synthetic intelligence, that would remodel ocean-conservation efforts which are a lot wanted on condition that most of the world’s fish species are in decline.
As soon as a really expensive, time-consuming course of carried out by observers on vessels, species monitoring utilizing superior expertise can now be so detailed that the information may even pinpoint the freshness of fish.
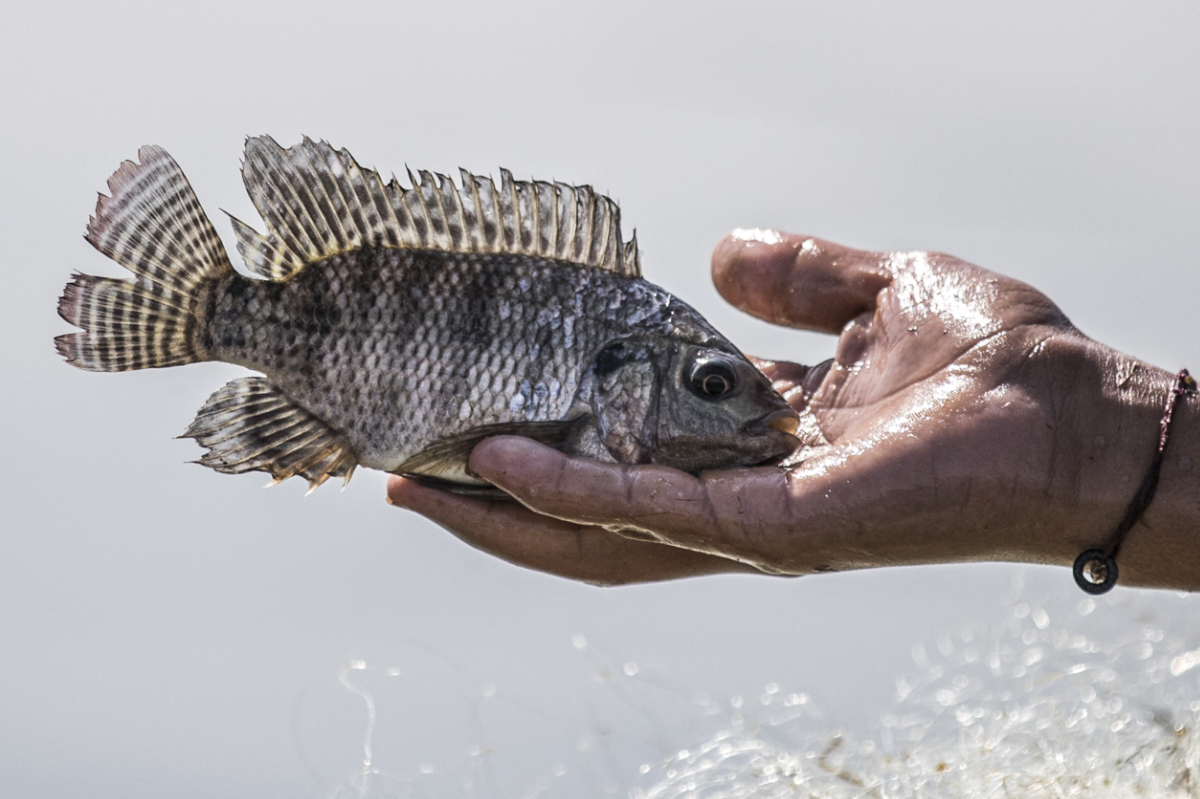

Edwin van Helmond, a fisheries scientist at Wageningen Marine Analysis, which is a part of WUR, mentioned that the potential for using AI and different applied sciences in supporting fisheries administration is large.
“The truth that detailed catch data might be collected by algorithms, with out the presence of specialists, makes knowledge assortment accessible in distant areas,” he advised Arab Information. “Information might be despatched or collected at a later stage or straight saved in a knowledge cloud and made remotely accessible for specialists.”
He believes such expertise may even significantly profit meals safety in the long run, which is a serious problem going through the Gulf area, and likewise the sustainable administration of pure sources, which begins with the gathering of ample knowledge.
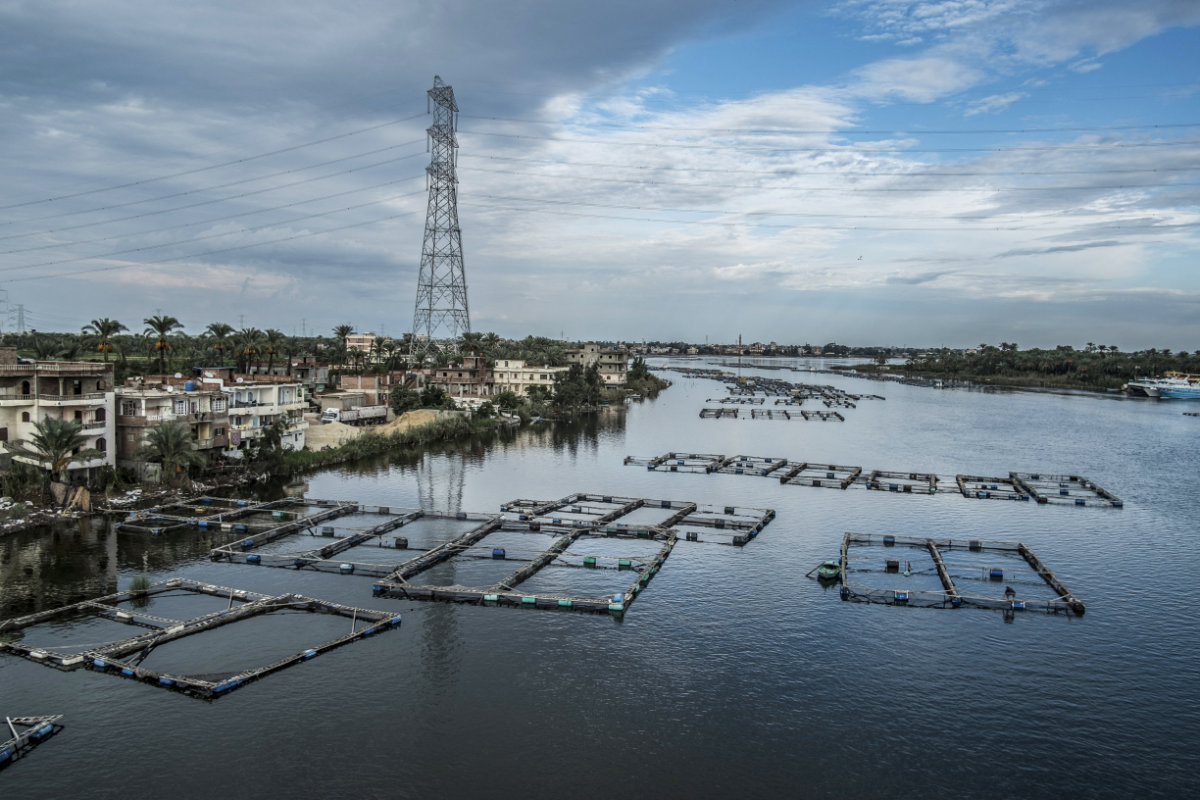

“To have the ability to carry out a superb evaluation of the accessible sources, on this case native fish shares, you want good knowledge,” he mentioned. “This consists of detailed catch data by species, catch weight, and size frequencies.
“These variables type the enter for any stock-assessment mannequin, and with these fashions you possibly can calculate sustainable harvest portions with out the hazard of over exploitation, which equates to sustainable administration of native fish shares and long-term meals safety.”
FAO is now attempting to make the expertise extra accessible in order that extra individuals within the business can profit from it, which in flip will assist the group broaden its knowledge units. Complete details about every species can be used to construct algorithms that may establish species and their places and acknowledge any adjustments.
FASTFACTS
Local weather change, diminishing fish shares and over-fishing are threatening coastal communities.
AI and cell apps are serving to fishermen worldwide interact in sustainable fishing practices.
As soon as such algorithms are developed, an app will enable customers to seek for particular species utilizing imagery that may unlock data such because the options of the species, meals values and different fisheries-related knowledge.
“Sooner or later, anybody, even a fisherman, may take photos of his catch, ship them off, get the species identification and, probably, additionally some metrics like the dimensions of the fish,” ultimately creating a portfolio of developments within the waters during which they work, Helmond mentioned.
The challenge within the Nile Basin, which is able to run for 3 to 5 years, may even have a look at sure nation necessities by way of languages, reporting and making certain knowledge units meet the specified ranges of safety.
Up to now, e. The system mirrors leisure fishing identification efforts in European rivers and lakes, the place communities fund programs that may establish catches and develop acceptable codes of follow amongst themselves.

“This then feeds again into understanding how properly the completely different rivers or lake programs are doing and which of them possibly should be augmented with hatchery-reared fish,” Friedman mentioned.
“It permits individuals to hyperlink up with others who wouldn’t have probably linked up prior to now.”
A key to success will likely be knowledge gathering by as many stakeholders as doable, mentioned Friedman. The resultant advantages for all these concerned would be the very best algorithms.
“There’s additionally a capability for us to begin to accumulate photos from across the Nile to inform individuals they will catch any such fish in good sizes and situation in a selected location,” he added. “So (this addresses) points about sustainability and likewise in search of market alternatives.”
The International Fishing Watch platform, a collaboration between Google, nonprofit environmental digital-mapping group SkyTruth and conservation group Oceana, was one of many first makes an attempt to mix AI with satellite tv for pc knowledge to look at fishing exercise.
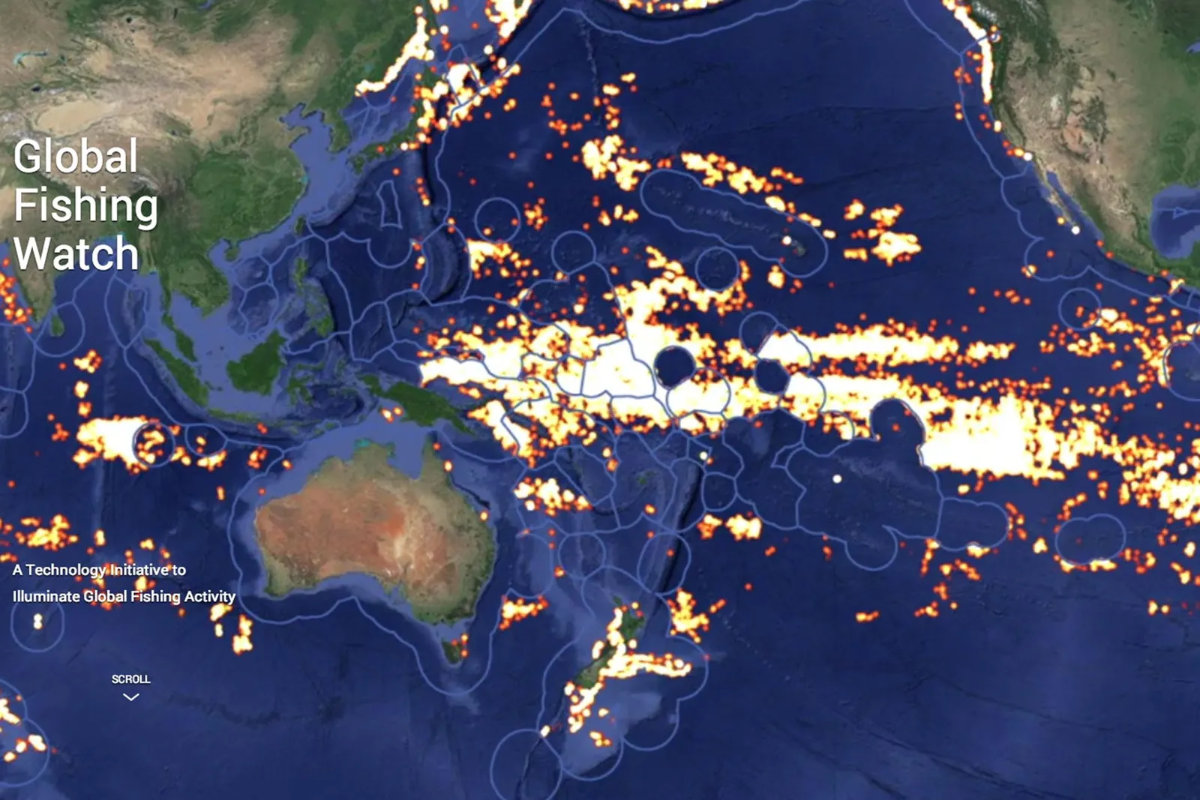
The expertise additionally presents hope for efforts to handle diminishing freshwater sources throughout the area, which has a number of the lowest ranges of recent water on the earth, primarily within the type of underground, non-renewable shares. Freshwater reserves have fallen by 60 % prior to now 4 many years, in accordance with FAO, and what stays is anticipated to decrease by 50 % by 2050.
Advances in expertise are anticipated to play a number one position within the creation of worldwide insurance policies to advertise sustainable fisheries and aquaculture and guarantee their development, with synthetic intelligence serving to to handle what’s now a world environmental concern. The info that’s gathered will enable fish and seafood retailers and prospects to be extra conscious of whether or not what they’re promoting and consuming is sustainable.
Innovation additionally holds the important thing to creating farming and the whole agri-food worth chain extra enticing, creating enterprise and employment alternatives and serving to the area to attain meals safety, sustainable agriculture and the targets of the UN’s Sustainable Growth Objectives.

FAO Director-Common Qu Dongyu believes the most recent collaborative challenge is a crucial step towards reaching this.
“A targeted and strengthened framework between FAO and Wageningen College and Analysis will enable our partnership to raised align efforts and sources for higher influence in assembly the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Growth Objectives,” he mentioned.
Along with the Nile challenge, FAO and WUR are collaborating on a number of different initiatives associated to the sustainable improvement of fisheries and aquaculture worth chains.
Within the African, Caribbean and Pacific States, for instance, a joint challenge referred to as FISH4ACP is offering experience on multi-stakeholder partnerships that’s contributing to meals safety and elevated vitamin, prosperity and job creation.
Simply final month, authorities in Saudi Arabia, which is chargeable for 49 % of the Gulf’s aquaculture, introduced they’re working to determine a regional middle for fisheries as a part of wider objectives to diversify the nationwide economic system and deal with meals safety.

Friedman mentioned that such initiatives have the potential to quickly unfold throughout the area and past.
“If we glance again by time, all of the regional guides that had been put collectively to know fisheries began off in sure areas and now are world,” he mentioned.
“I believe we could have the identical factor occur not only for the Nile, however for inshore fisheries, pelagic (open sea) fisheries and so forth, primarily based on the alternatives that AI will supply us.”
[ad_2]
Source link


