[ad_1]
Nepali economic system has skilled a liquidity crunch because the starting of the present monetary 12 months. Even with repeated coverage measures undertaken by the Nepal Rastra Financial institution (NRB) to ease the liquidity stress, the economic system continues to really feel the extended crunch.
Introduction
Liquidity is the provision of money or close to cash property that the Banks and Monetary Establishments (BFIs) maintain to fulfill the demand for money for his or her depositor or borrower. The depositors park their extra funds in banks for future use, whereas debtors are money deficit items who want funds for varied monetary and financial actions within the economic system. An economic system is claimed to be in a liquidity disaster if the BFIs are unable to fulfill the demand for money from their prospects.
Nepali economic system has skilled a liquidity crunch because the starting of the present monetary 12 months. Even with repeated coverage measures undertaken by the Nepal Rastra Financial institution (NRB) to ease the liquidity stress, the economic system continues to really feel the extended crunch. To additional unpack the problem, this text goals to discover elements resulting in liquidity crunch and challenge a manner ahead.
The present liquidity crunch doesn’t imply that BFIs don’t have sufficient liquidity to fulfill money demanded by the depositors, as web liquidity of BFIs stands at 21.78%, which is above the regulatory requirement as mandated by Nepal Rastra Financial institution. Nevertheless, the present disaster is totally different, it’s the incapability of banks to satisfy the demand for funds by debtors as enterprise actions expanded post-pandemic.
Background
Within the first eight months of the present monetary, the credit score disbursed by BFIs elevated by 10.5% to NPR 4.60 trillion (USD 38 billions), whereas deposit elevated by 4.1% to NPR 4.85 trillion (USD 40 billions) within the evaluation interval. Thus, growing demand of funds as in comparison with provide has contributed to the tight liquidity state of affairs within the economic system. The lending fee elevated to eight.98% from 6.84% in the identical interval within the earlier 12 months, highlighting the surplus stress on liquidity.
It led to rise within the Credit score-to-Deposit ratio to 90.87%, which is above the higher restrict (90%) as directed by the Nepal Rastra Financial institution. Moreover, the interbank fee has risen to six.56% and has constantly been above its higher restrict, thereby exhibiting persistent stress on financial institution fund and lack of liquidity.
Determine 1: Pattern – Interbank rate of interest in FY 2021/22
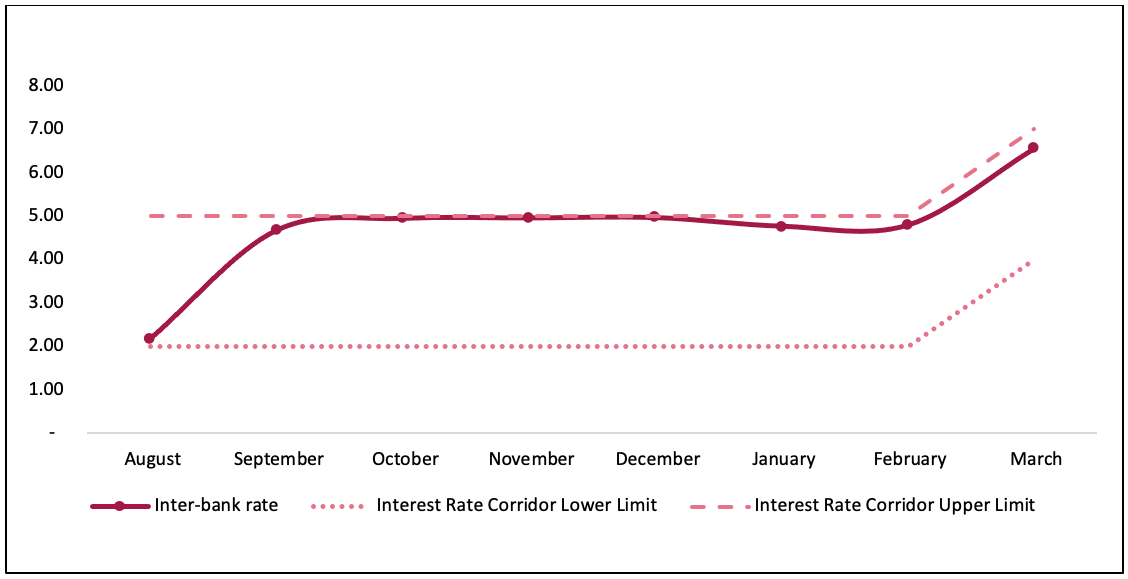
Supply: Present Macroeconomic and Monetary Scenario Tables – (Based mostly on Eight Months knowledge from 2021-22), NRB
Determinants of liquidity and understanding the liquidity crunch
The persevering with liquidity crunch is a recurring occasion within the Nepali economic system and might be attributed to the multidimensional structural issues current within the economic system, as mentioned under. Such issues are associated to the supply of liquidity for the banking system, therefore are detrimental to the availability of liquidity within the economic system.
Financial savings
The extent of financial savings within the economic system contributes on to deposits within the banking system and therefore to the availability of loanable funds to BFIs. An estimate by the Worldwide Labor Group predicts that round 1.6 million to 2 million folks in Nepal will both lose their jobs or have jobs that pay decrease wages, resulting in a rise in unemployment and the decline in revenue, translating into decrease financial savings within the economic system. In response to the Financial Survey 2020-21, the Gross Nationwide Financial savings of 31.4% of GDP in FY 2020-21, whereas it was 42.1% of GDP in FY 2019-20. Subsequently, as a result of deteriorating nationwide financial savings, banks’ deposits weren’t capable of preserve tempo with the demand for credit score inflicting liquidity scarcity.
Authorities spending
The federal government expenditure plan has the potential to extend liquidity out there as authorities spending is channelized by means of BFIs by way of deposits, thereby contributing to the availability of funds to BFIs however it will possibly solely occur if the plan is realized in actuality. For instance, in FY 2020-21 the federal government deliberate to spend NPR 1.47 trillion (USD 12.2 billions), however in keeping with the NRB statistics, complete authorities expenditure amounted to NPR 1.18 trillion (USD 9.8 billions) solely, thus exhibiting the lack of the federal government to spend as deliberate. Moreover, in FY 2021-22, the federal government has managed to spend 27.45% of the allotted capital funds. So, the federal government’s incapability to mobilize funds within the economic system has contributed to a chronic liquidity disaster in Nepal.
Remittance
Remittance has a constructive impression on the home liquidity place as they’re straight deposited within the home banking system, thereby growing the power of banks to mobilize funds within the economic system. Although the stream of remittances decreased by 1.7% within the present monetary 12 months, it had elevated by 8.7% in the identical interval of the earlier 12 months. Moreover, nearly half of the remittances despatched to Nepal are by means of casual channels. A serious portion of remittances are usually not channelized by means of the banking sector mixed with lowering official influx has contributed to a lowered skill of BFIs to mobilize funds within the economic system which has led to a liquidity crunch.
Foreign exchange
The supply of international trade reserves with the Central Financial institution enhance’s skill to stabilize market liquidity. Nepal Rastra Financial institution injected liquidity value NPR 147.14 billion (USD 1.22 billion) by means of a web sale of USD 1.22 billion from international trade reserves, growing liquidity within the economic system. Nevertheless, in the identical interval, the international trade reserve decreased by 18.5% to USD 9.58 billion as commerce deficit elevated by 34.5% in FY 2021-22, thereby limiting the power of the central financial institution to stabilize the liquidity place.
Steadiness of Fee
The growing Steadiness of Fee (BOP) deficit has turn out to be a priority for the economic system because the deficit elevated to NPR 258.64 billion (USD 2.1 billion), whereas BOP was in surplus of NPR 68.01 billion (USD 562 million) in the identical interval the earlier 12 months. An growing BOP deficit implies leakage of home funds to the international economic system, as funds made to companies overseas for imports are usually not offset by earnings made by means of exports. Subsequently, growing commerce deficit that drains out the liquidity from the economic system, resulting in a scarcity in liquidity.
NRB liquidity injection and its constraints
Nepal Rastra Financial institution, the Central Financial institution of Nepal has injected a complete of NPR 5070.76 billion in liquidity by utilizing financial coverage devices like repo, and Standing Liquidity Facility (SLF). Regardless of the injection of huge quantities of cash to stabilize stress on liquidity, the issue persists. Nevertheless, the central financial institution is proscribed in its skill to inject liquidity as demanded as a result of growing inflation and commerce deficit.
The central financial institution is liable for sustaining worth and exterior sector stability within the economic system. In response to NRB statistics, inflation elevated to 7.14% within the present fiscal 12 months, surpassing Authorities of Nepal’s projection of 6.5% whereas commerce deficit rose to NPR 1.16 trillion (USD 9.6 billion). To restrict the hostile impacts of accelerating inflation and commerce deficit, Nepal Rastra Financial institution has limitations on injecting liquidity to satisfy the growing demand for liquidity within the economic system.
Outlook
The liquidity crunch throughout the Nepali economic system had been exacerbated ever because the financial actions expanded after the COVID-19 induced lockdowns. Given the existence of structural issues within the economic system, the policymakers ought to concentrate on long-term options which embrace formalizing the casual economic system and growing entry to banking and monetary companies to raised mobilize unaccounted funds and transactions into the banking system.
In the meantime, growing authorities expenditure can enhance liquidity circumstances instantly, as it’s going to mobilize idle funds from the federal government treasury into the economic system, thereby growing liquidity. Moreover, Nepal Rastra Financial institution can limit stream of funds to unproductive sectors, because it will increase inflation with out growing financial exercise. Thus, diverting funds to productive sector will contribute to unfulfilled demand for funds, thereby easing stress on market liquidity.
[ad_2]
Source link


