[ad_1]

Amongst adults vaccinated towards COVID-19, the percentages of creating lengthy COVID amid the omicron wave have been about 20 % to 50 % decrease than in the course of the delta interval, with variability based mostly on age and time since vaccination.
The discovering comes from a case-control observational research revealed this week in The Lancet by researchers at Kings Faculty London. The research discovered that about 4.5 % of the omicron breakthrough circumstances resulted in lengthy COVID, whereas 10.8 % of delta breakthrough circumstances resulted within the long-term situation.
Whereas the information could seem somewhat reassuring to these nursing a breakthrough omicron an infection, it is chilly consolation for public well being general for the reason that omicron coronavirus variant is rather more transmissible than delta.
“Way more individuals have been contaminated first with omicron than with delta,” Kevin McConway, an emeritus professor of utilized statistics on the Open College, stated in a press release. “So even when the share of contaminated individuals who acquired lengthy COVID in the course of the two waves is on the size that these researchers report—and it could be—the precise numbers of individuals reporting lengthy COVID after first being contaminated throughout omicron continues to be far bigger than throughout delta.”
For The Lancet research, researchers examined self-reported symptom knowledge from 56,003 UK adults who have been first contaminated with SARS-CoV-2 in the course of the omicron wave and 41,361 UK adults who have been initially contaminated in the course of the delta interval.
The researchers, led by Claire Steves, a senior scientific lecturer at King’s Faculty London, outlined lengthy COVID as having new or ongoing signs 4 weeks or extra after the beginning of acute COVID-19, which is the way it’s outlined within the US Nationwide Institute for Well being and Care Excellence tips.
Vital burden
When the researchers adjusted for age, time since vaccination, and different health-related elements, the relative odds of creating lengthy COVID after omicron ranged from round 23 % to 50 %. The chances have been finest when individuals have been nearer to vaccination (inside lower than three months) and aged 60 and older.
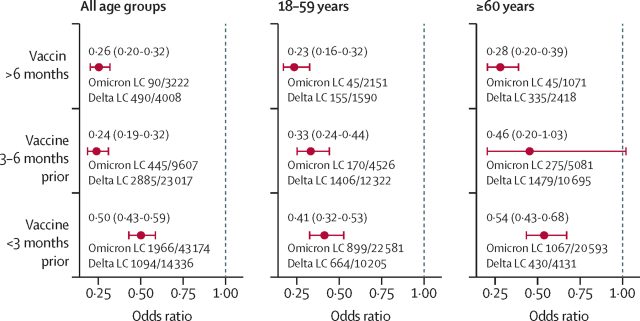
The research has limitations, the obvious of which is that it’s based mostly on self-reported symptom knowledge and would not dive into the severity of the lengthy COVID circumstances. There was additionally inadequate knowledge to take a look at lengthy COVID charges amongst unvaccinated individuals, and the research didn’t embody knowledge on charges in kids.
The research was additionally completed in the course of the BA.1 wave, as David Pressure, scientific senior lecturer on the College of Exeter Medical College, famous in a press release. The following omicron subvariants, together with BA.2, BA.2.12.1, and the up-and-coming BA.4 and BA.5, could have completely different profiles relating to lengthy COVID dangers.
Nonetheless, even when the estimate of 4.5 % holds up over time, that interprets to lots of people creating lengthy COVID. This “creates a big public well being burden of this illness with no recognized remedy, and even dependable diagnostic take a look at,” Pressure added.
Steves echoed the sentiment, saying in a press release: “The omicron variant seems considerably much less prone to trigger long-COVID than earlier variants, however nonetheless 1 in 23 individuals who catch COVID-19 go on to have signs for greater than 4 weeks. Given the numbers of individuals affected, it is essential that we proceed to assist them at work, at dwelling, and throughout the [National Health Service].”
[ad_2]
Source link


