[ad_1]
The PSLV really took off at 6.02pm. Purpose: The Collision Avoidance Evaluation (COLA) had pointed to a threat of collision between onboard payloads with area objects if the lift-off occurred on the supposed time.
“Essentially the most regarding conjunctions had been with Starlink and Fengyun particles, particularly with Starlink 2701 because the closest strategy was discovered to be inside 100m throughout ascent section,” data from the Isro System for Secure and Sustainable House Operation and Administration (IS4OM) exhibits.
If the lift-off occurred at 6.01pm as a substitute of 6pm, there would nonetheless be a threat of collision. “…A detailed conjunction between the PSLV-c53 passenger satellite tv for pc SCOOB-1 with Starlink 1705 and Iceye-X6 (a Finnish microsatellite) was detected in its orbital section,” IS4OM report exhibits.
Secure lift-off, subsequently, was proposed to be 6.02pm, and it proved proper with all payloads being positioned within the desired orbits. COLA and deferred lift-off, nonetheless, just isn’t distinctive to the June 30 mission.
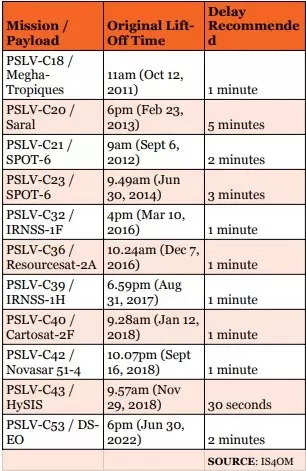
In response to Isro, there have been at the very least 10 different PSLV missions — between 2011 and 2022 — that needed to be delayed owing to collision threat.
Essentially the most a launch was delay by was 5 minutes (the PSLV-C20 mission carrying Saral satellite tv for pc on February 23, 2013, whereas the least time distinction was 30 seconds, for PSLV-C43 carrying HySIS satellite tv for pc on November 29, 2018. Most had been one-minute delays whereas one 2014 mission was delayed by three minutes and two, together with the C53 mission, had been delayed by two minutes ( see desk).
Isro Chairman S Somanath, on the formal inauguration of IS4OM mentioned on Monday: “House exercise is growing and satellites should go to area for us to leverage know-how. This can give rise to area particles, however we’re setting up techniques to deal with this. IS4OM is barely step one.”
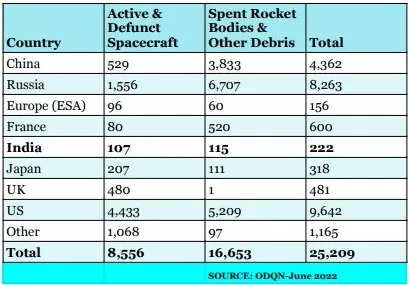
Actually, in accordance with the NASA Orbital Particles Quarterly Information (ODQN) for June 2022, there are 25,209 area objects — 8,556 energetic and defunct spacecraft and 16,653 spent rocket our bodies and different catalogued particles — with eight nations, together with India contributing probably the most.
Whereas the US has probably the most objects 9,642, India has 222. China and Russia are different nations to have objects in 4 digits. Europe, via the European House Company (ESA), France, Japan, UK and India have lower than 1,000 objects ( see desk).
[ad_2]
Source link


