[ad_1]
Nepal Rastra Financial institution (NRB) launched the financial coverage for the FY 2022/23 retaining in thoughts the present macroeconomic situation of the financial system. Maintaining in thoughts the lockdown imposed by the pandemic, the earlier two financial insurance policies had been expansionary in nature focused for financial restoration by selling consumption and manufacturing. Nonetheless, as a result of liberal nature of financial coverage and growing value of petroleum merchandise, inflation surged from 4.4% originally of the fiscal yr (mid-August, 2021) as much as 8.6% in the direction of to finish of the earlier fiscal yr (mid-June, 2022).
Determine 1: Development on inflation
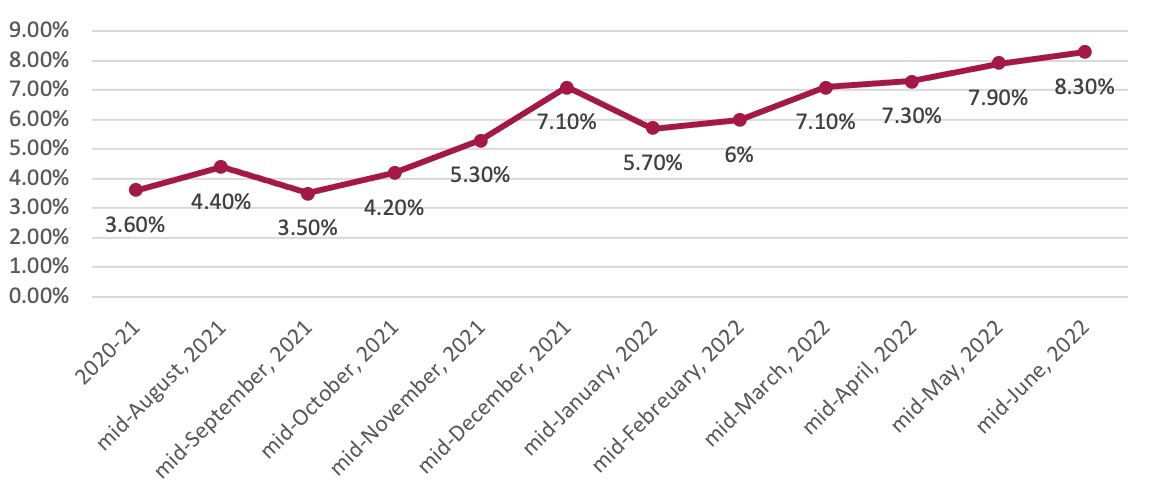 Supply: Financial Coverage 2022/23, Nepal Rastra Financial institution
Supply: Financial Coverage 2022/23, Nepal Rastra Financial institution
In the identical time interval, credit score growth by Banks and Monetary Establishments (BFIs) elevated import resulting in surge within the commerce deficit, inflicting woes for coverage maker. The commerce deficit elevated by 25% to NPR 1577 billion (USD 12.34 billion) which led to deterioration within the foreign exchange reserve to NPR 1176 billion (USD 9.20 billion). Such stage of foreign exchange reserve can finance, import for lower than 6.6-months whereas the NRB has set the goal to take care of foreign exchange reserve to maintain 7-months of imports.
Given the deteriorating macroeconomic indicators which posed a menace to the soundness of the home financial system, the central financial institution has adopted a contractionary financial coverage. Such stance has been adopted to regulate the unstable financial system fueled by an enormous surge in imports-based consumption and the impact of the continued conflict between Russia and Ukraine. Subsequently, the stance of the financial coverage has been cautiously tightened with the target “to advertise macroeconomic stability whereas sustaining value and exterior sector stability, and to assist financial development by way of growing productiveness by channelizing monetary sources to productive sectors”.
Such stance has been adopted to realize the authorities’s financial development goal of 8% and inflation goal of seven% for the FY 2022/23.
Credit score Creation
To realize the financial development goal as envisioned by the funds of 2022/23, NRB will likely be increasing credit score to assist growth of financial actions. The financial coverage has focused credit score in the direction of non-public sector to develop 12.6%, the place it was 19% within the earlier financial coverage. The discount in credit score creation could be defined by insufficient development in deposits in BFIs. A decrease credit score development will have an effect on the expansion of BFIs and their profitability within the upcoming fiscal yr. Moreover, it would restrict credit score given to the non-public sector to finance imports, thereby limiting commerce deficit.
Determine 2: Development on Non-public sector credit score development
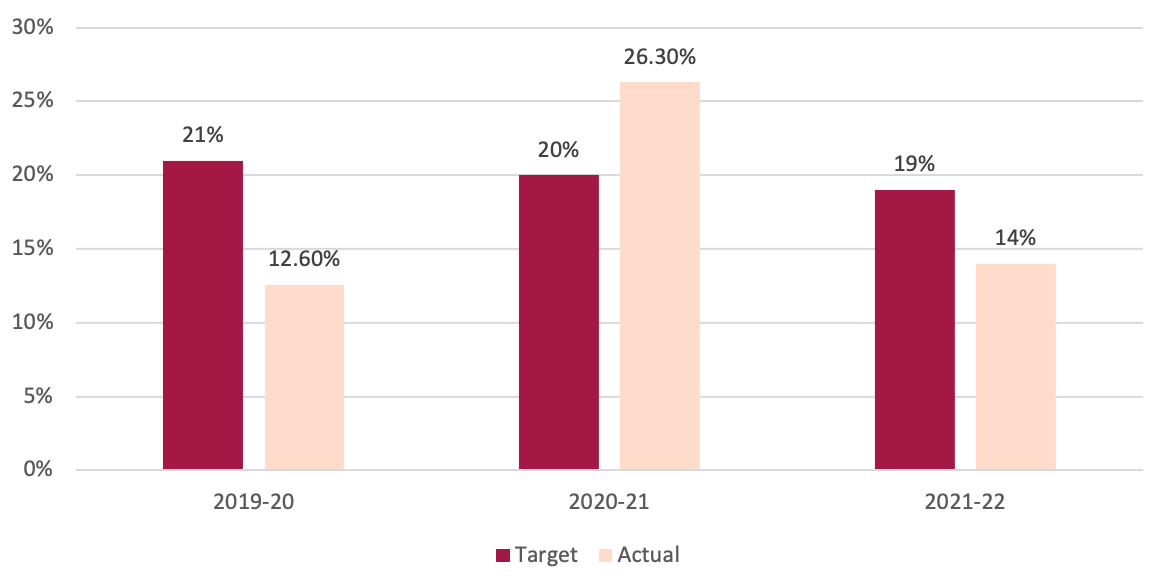 Supply: Financial Coverage 2022-23. Nepal Rastra Financial institution
Supply: Financial Coverage 2022-23. Nepal Rastra Financial institution
The precise credit score development within the non-public sector was decrease than the goal in FY 2019-20 as a result of halt in financial exercise owing to the onset of the pandemic. Precise credit score development to personal sector crossed its goal in FY 2020-21, as financial actions started to get better following the comfort in lockdown. Nonetheless, in FY 2021-22 credit score development remained decrease than the goal resulting from insufficient liquidity within the banking system.
Equally, in step with focused credit score development, the expansion price of broad cash provide has been set to 12%, whereas it was 18% within the earlier financial coverage. A lower in development of cash provide has been formulated to regulate growing inflation to curtail it inside the goal set by the funds.
Liquidity
To advertise public belief by defending public deposits in BFIs, the financial coverage has elevated the minimal requirement of liquid belongings that the BFIs should maintain. The Money Reserve Ratio (CRR), which is the minimal money that BFIs should preserve as deposit at NRB, has been elevated from 3% to 4% of the overall deposit base of a financial institution. Equally, the Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), which is the minimal liquid belongings that BFIs a lot maintain as authorities safety, has been elevated to 12% for industrial banks and 10% for growth banks and monetary establishment.
Such enhance in necessary liquidity reserve to be maintained by BFIs will enhance price for BFIs, as these belongings naked no or low returns to BFIs. Moreover, it would scale back loanable funds that BFIs can lend, thereby limiting liquidity within the financial system.
Curiosity Price Hall
Interbank price will proceed as operational goal and it is going to be maintained inside the vary of the Curiosity Price Hall (IRC). The higher and decrease restrict of IRC are financial institution price and deposit assortment price, respectively. A change in IRC impacts the rate of interest at which BFIs lend cash to debtors. To restrict the credit score going into unproductive sector, the financial coverage has elevated operational goal of the IRC by 1.5%. Financial institution price, coverage price (repo price) and deposit assortment price has been elevated to eight.5%, 7% and 5.5% respectively. Such charges had been 7%, 5.5% and 4% within the earlier fiscal yr.
Determine 3: Development on Curiosity Price Hall
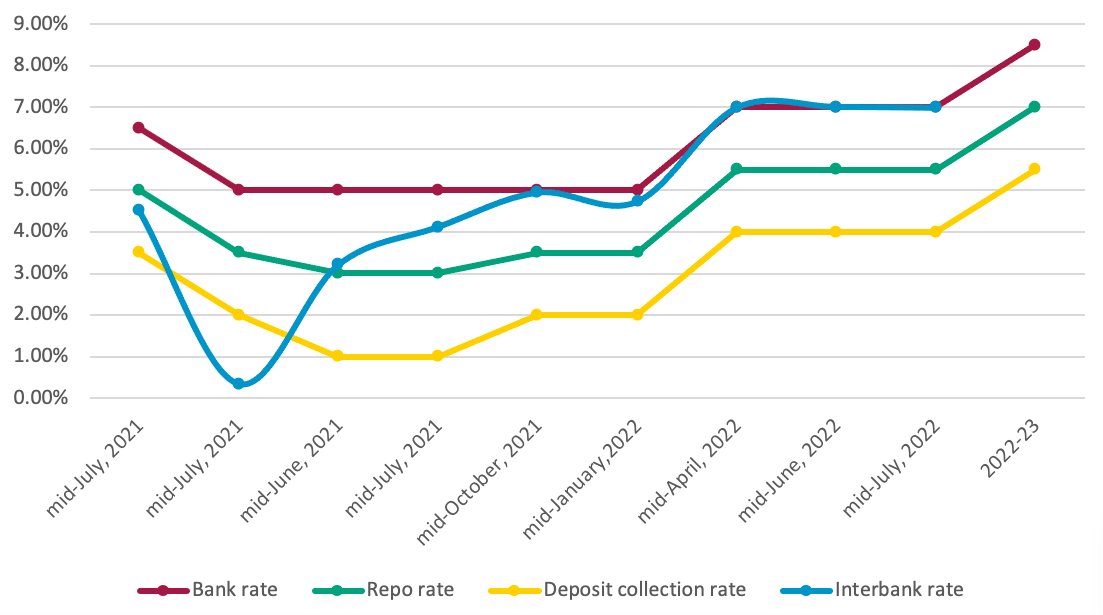
Supply: Financial Coverage 2022-23, Nepal Rastra Financial institution
The interbank price remained excessive and on par with an higher restrict of the rate of interest hall, i.e., financial institution rake, reflecting extreme stress on home liquidity within the banking system.
NRB has made provision to intervene through Open Market Operation (OMO) provided that interbank rate of interest fluctuates by greater than 2% of the focused coverage price (repo price). Equally, NRB will take up liquidity through a deposit assortment mechanism provided that the interbank rate of interest decreases by greater than 3% of the coverage price (repo price).
The rise in coverage charges will enhance the speed at which enterprise and client can avail credit score from BFIs. It’ll enhance prices for import-based consumption, thereby curbing import and inflation within the financial system.
Refinance and Concessional Loans
As financial actions are recovering from the lows of a pandemic, the refinance facility and concessional loans given by NRB for industries affected by COVID-19 pandemic will likely be step by step rolled backed. The excellent quantity of refinance offered by NRB reached NPR 114.97 billion (USD 900 million) and complete concessional loans remained at NPR 215.91 billion (USD 1.69 billion) until mid-June, 2022. The financial coverage has confined such sponsored facility to agriculture, exports and sectors that are but to get better from the opposed impact of the pandemic.
Productive sector lending
As acknowledged within the goal of the financial coverage, emphasis will likely be given in the direction of mobilizing low-cost credit score to the productive sector. Productive sector is the sector during which greater than 7% of the overall uncooked supplies used are from home sources. BFIs extending credit score as much as NPR 20 million (USD 156 thousand) to productive sector can cost a most of two% above the bottom price.
The Micro Small and Medium (MSME) enterprise having to repay loans as much as NPR 50 million (USD 391 thousand) is not going to be charged an additional penal rate of interest upon compensation of due loans as much as mid-October 2022. Equally, MFIs can cost a most of two% above base price whereas extending credit score to native cooperative teams.
Capital Requirement
Within the earlier financial coverage, NRB had launched provision of CD ratio (Credit score-to-Deposit) of 90% to be maintained by BFIs. It elevated the capability of BFIs to offer credit score for financial restoration, nevertheless, resulting from growing stress on liquidity many BFIs crossed the 90% mark. To ease the stress on CD ratio, the financial coverage has allowed bonds and debenture to be included as deposits whereas calculating the CD ratio. It’ll launch some liquidity within the banking system which can be utilized for lending functions.
The counter cyclical buffer suspended in the course of the onset of the pandemic to launch additional loanable fund for lending has been reimposed. Now BFIs must preserve additional capital of two% of their Threat-Weighted-Belongings (RWA), due to this fact, growing the minimal capital adequacy from 11% to 13% of RWA.
Moreover, Micro Monetary Establishments (MFIs) will likely be allowed to challenge bonds to lift capital for lending. The utmost worth of bonds issued can at most could be equal to the quantity of capital held by MFIs.
Remittances
NRB has mandated that migrant staff demanding international alternate have to have a checking account denominated in Nepali forex. Such account needs to be linked with the remittance receiving account in order to advertise the formal influx of remittance. The amenities acquired by such account will likely be reviewed in order that further facility could be offered to migrant staff sending remittance by way of the formal banking sector. Such provision will promote the formal influx of remittances, which is able to ease stress on depleting foreign exchange reserves and assist restore stability cost deficit.
Capital market and actual state
The one obliger, margin lending, which was restricted to 4/12 rule has been relaxed. Now margin lending restrict has been modified to 12/12 i.e., any particular person can avail credit score as much as NPR 120 million (USD 939 thousand) from a number of monetary establishment. It’ll ease the method with which inventory market buyers can avail credit score to put money into NEPSE, thereby it’s anticipated that NEPSE index to rise sooner or later.
The Mortgage to Worth (LTV) ratio, which a borrower can borrow for development of the brand new home, has been tightened. Earlier, the LTV was 40% for home consumers in Kathmandu and 50% exterior Kathmandu. This has been decreased to 30% and 40%, respectively. It’ll restrict funds directed in the direction of the true property sector, thereby releasing funds to be directed in the direction of productive sector.
Outlook
Because the macroeconomic indicators deteriorated prior to now, it has elevated uncertainty concerning the prospect of a full financial restoration. The financial coverage has adopted cautionary tightening by elevating rate of interest to advertise macroeconomic stability whereas sustaining value and exterior sector stability. The liquidity situation is anticipated to remain tight as credit score development targets have been revised downwards to regulate for growing commerce deficit and inflation. The stance adopted will be capable to management inflation inside the goal envisioned within the funds, however reaching financial development price of 8% within the upcoming fiscal yr can turn out to be difficult.
Particular emphasis has been given to channelize monetary useful resource to the productive sector to reinforce productive capability of the financial system with the intention of lowering reliance on imports. Selling growth of productive sector will contribute in the direction of producing employment and obtain sustainable financial development in the long term. Subsequently, the financial coverage has acknowledged the tradeoff between financial development and stability and has prioritized financial stability with particular give attention to the productive sector for enhancing the productive capability of the financial system to realize sustainable financial growth.
Compiled by Ashish Gupta, Aspiring beed at Beed Administration.
[ad_2]
Source link


