[ad_1]
This research has three elements—an open stepped-wedge cluster-randomised managed trial to guage the effectiveness of private safety bundle in decreasing the prevalence of Plasmodium spp. an infection in forest-going MMPs and people of their residing villages; a mixed-methods research to discover the acceptability of a private safety bundle, feasibility of implementing a private safety bundle as a vector management intervention, and data, perspective and follow of MMPs relating to malaria prevention; and cost-analysis to find out the cost-effectiveness of implementing a private safety bundle. The principle textual content of this paper focuses on the trial with different research elements and information assortment instruments detailed in Extra file 1.
Intervention
The intervention within the trial is a private safety bundle for use by the forest-going MMPs for prevention of Plasmodium spp. an infection. The bundle was designed in session with related implementing companions: Nationwide Malaria Programmes: Cambodia Nationwide Middle for Parasitology Entomology and Malaria Management and Laos Middle of Malariology Parasitology and Entomology; and non-governmental organizations: Well being Poverty Motion (HPA), PEDA and CHIAs in Cambodia and Lao PDR.
The intervention bundle contains three objects—WHO pre-qualified long-lasting insecticidal hammock web (LLIHN) (high-density polyester monofilament yarn blended with 2% (w/w) permethrin), two insect repellent bottles (1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 2-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-methylpropylester, often known as Icaridin), and an MMP-tailored well being communication pamphlet. Along with the pamphlet, behavioural change communication may even be delivered within the types of well being communication classes in teams and well being communication posters posted at or across the MMP’s workplaces. The intervention bundle shall be distributed via the malaria volunteers operated by implementing companions.
Outcomes
The first final result of this trial is the prevalence of Plasmodium spp. an infection recognized by speedy diagnostic take a look at (RDT). Secondary outcomes of this trial embody symptomatic malaria an infection recognized by RDT, Plasmodium spp. an infection as decided by polymerase chain response (PCR), Plasmodium spp. infections with drug resistance mutations, prevalence and ranges of antibodies to Plasmodium spp. and mosquito salivary antigens (Desk 1).
End result assortment plan
Information required to find out the first final result of the research, Plasmodium spp. an infection recognized by RDT, and secondary final result 2A (Desk 1) shall be recorded by malaria volunteers of their routine malaria case register, which is a standardized kind developed and utilized by the implementing companions. When a person presents to a malaria volunteer for a RDT for malaria, they are going to be requested to offer one other two drops of blood onto a bit of filter paper. Blood spots shall be collected on filter papers from all consented people instantly earlier than they’ve acquired the RDT take a look at from the malaria volunteer.
Used RDT cassettes and dried blood spots shall be stored and saved the place attainable to extract DNA and antibodies to find out secondary outcomes 2B, 2C, 2D, 2E, 2F, and 2G utilizing PCR and ELISA strategies as beforehand described [16, 19,20,21].
Research setting and inhabitants
Villages and worksites in malaria endemic areas of Cambodia (Preah Vihear, Stung Treng and Ratanakiri Provinces) and Lao PDR (Attapeu, Cahmpasack, Khammouane, Saravanh and Savannakhet provinces) shall be included on this trial (Fig. 1). The members shall be forest-going MMPs [11] together with—conventional slash-and-burn and paddy area farming communities, seasonal agricultural laborers, forest staff within the casual sector, transient or cellular camp residents related to business tasks (street/pipeline building, large-scale logging, and many others.), and formal and casual cross-border migrant staff.
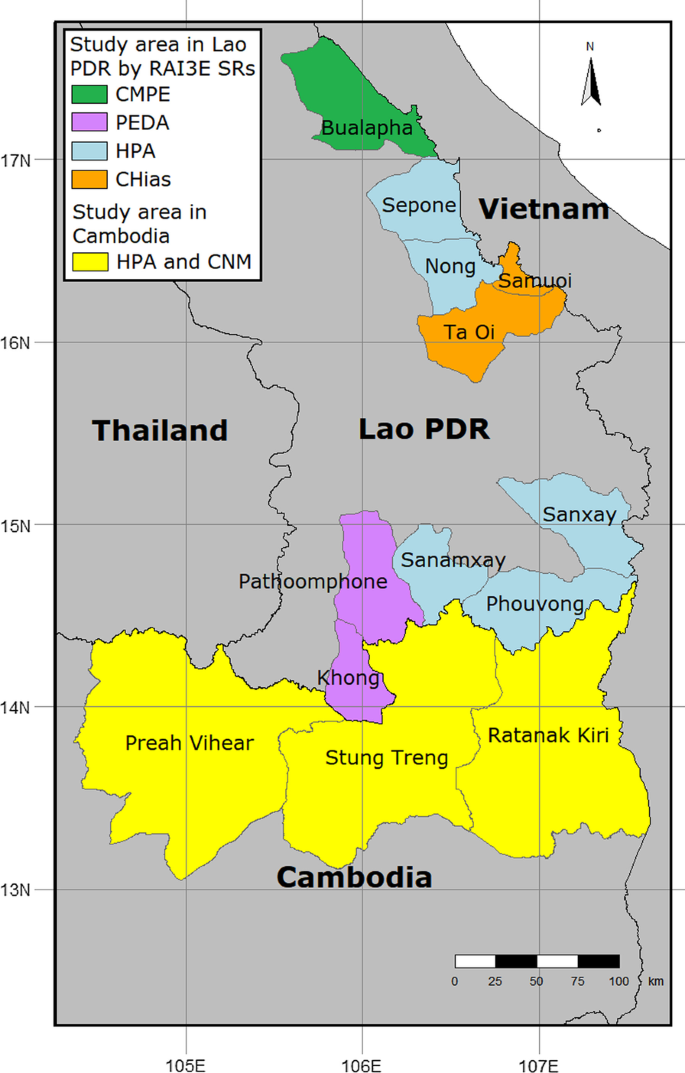
Map of the research areas (Map generated utilizing the tmap bundle in R model 3.6.1 utilizing base maps from the GADM database of International Administrative Areas, model 2.8. URL: www.gadm.org)
Eligibility standards
The provinces included within the trial have been chosen based mostly on the presence of malaria volunteer community within the province, capability of implementing companions for area implementation, excessive malaria burden and excessive MMP actions.
Villages/worksites managed by the implementing associate within the chosen provinces shall be screened towards the next exclusion standards by investigators and implementing associate employees. A village/worksite shall be excluded from the research if it: (1) has no malaria circumstances or annual parasite incidence lower than 1 in any of the previous three years (2018–2020), (2) has no MMPs, (3) has no malaria volunteer actively working within the village/worksite, (4) has a authorities well being facility for malaria companies, or (5) has one other malaria volunteer program operated by any organizations aside from implementing associate.
After the village/worksite has been chosen, the MMPs with the next standards shall be included within the research for receiving the intervention (i.e. private safety bundle): (1) presently residing within the chosen villages/worksites, and (2) being any of the next sorts of staff—conventional slash-and-burn and paddy area farming communities visiting their forest farms (generally ethnic minority teams), seasonal agricultural laborers, forest staff within the casual sector (hunters, small-scale gem/gold miners, individuals gathering forest merchandise (treasured timber, building timber, rattan/bamboo), transient or cellular camp residents related to business tasks (street/pipeline building, large-scale logging, deep seaport tasks, and many others.), and formal and casual cross-border migrant staff.
Research design and pattern
The research design for the trial part of this research is an open stepped-wedge cluster-randomised managed trial, randomised on the village/worksite degree and carried out over a 12-month interval, following a one-month baseline interval (Fig. 2). The research shall be carried out between March 2022 and February 2023. The non-public safety bundle for MMPs shall be carried out sequentially in a minimal of 488 villages serviced by roughly 488 Village Malaria Staff (~ 428 in Lao PDR and ~ 60 in Cambodia). Villages from every nation shall be randomised into 11 blocks, with blocks transitioned in random order from management (no private safety bundle) to intervention (with private safety bundle) states at month-to-month intervals (10 blocks of 44 villages for the primary 10 steps and a block of 48 villages transitioned on the remaining step). All eligible MMPs in collaborating villages will obtain the intervention through the research, however the month at which they transition from a management to the intervention state shall be randomised.
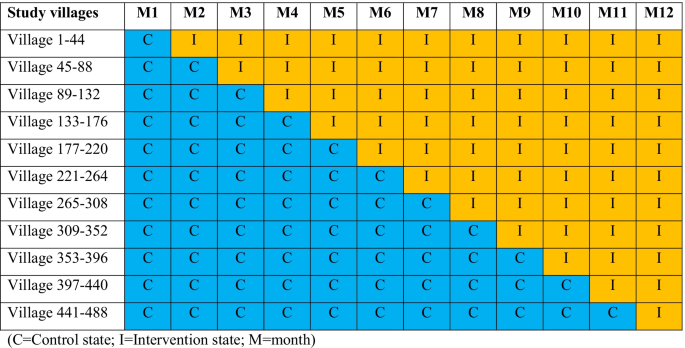
Timeline for stepwise implementation of the non-public safety bundle within the chosen villages
Research energy
It’s estimated that roughly 11 RDTs per thirty days shall be undertaken at every research web site (village/worksite), yielding an approximate complete of 64,416 RDT exams over 12 months. Given this pattern dimension, the trial will be capable to detect a minimal relative discount of 34% within the odds (OR = 0.66) of RDT-detectable malaria an infection attributable to the intervention (assuming a village intraclass correlation [ICC] = 0.42 [16]; 5% significance; 90% energy and 1% RDT malaria prevalence). Energy estimation was based mostly on estimation of an intervention impact utilizing trial information from a stepped-wedge cluster-randomised design assuming evaluation by generalized linear combined modelling (GLMM).
Information evaluation
Information entry shall be managed in a REDCap database developed by Burnet Institute. For the stepped-wedged cluster-randomised trial, each descriptive and first final result trial analyses shall be carried out. To evaluate the effectiveness of distribution of the non-public safety bundle, distinction within the prevalence of malaria an infection shall be estimated throughout intervention and management durations utilizing GLMM (logit hyperlink perform and binomial distribution) with time-varying fastened elements for intervention standing and time, and crossed random results for village and time carried out to account for the dependencies inherent within the information given the stepped-wedge design. We may even discover any village-specific heterogeneity in impact by specifying a random impact for the intervention and the extent to which effectiveness of intervention is time-dependent. GLMM shall be prolonged to incorporate mannequin phrases for nation (primary and interplay results), and these will used to evaluate the extent of country-specific heterogeneity in intervention impact. Analyses of secondary outcomes may even contain multi-level modelling (i.e., linear combined modelling (LMM) and GLMM). Statistical evaluation shall be carried out utilizing Stata model 17.
[ad_2]
Source link


