[ad_1]
NASA, ESA, STScI, Wenlei Chen, Patrick Kelly
Over the previous few many years, we have gotten a lot better at observing supernovae as they’re occurring. Orbiting telescopes can now choose up the high-energy photons emitted and determine their supply, permitting different telescopes to make fast observations. And a few automated survey telescopes have imaged the identical components of the sky evening after evening, permitting picture evaluation software program to acknowledge new sources of sunshine.
NASA, ESA, STScI, Wenlei Chen, Patrick Kelly
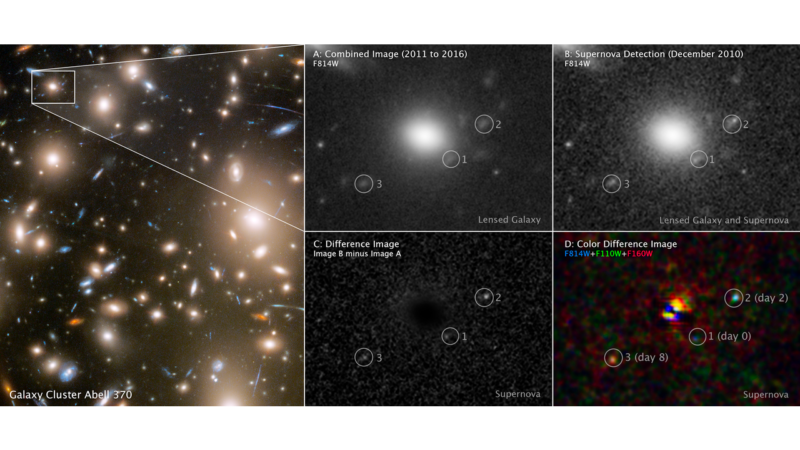
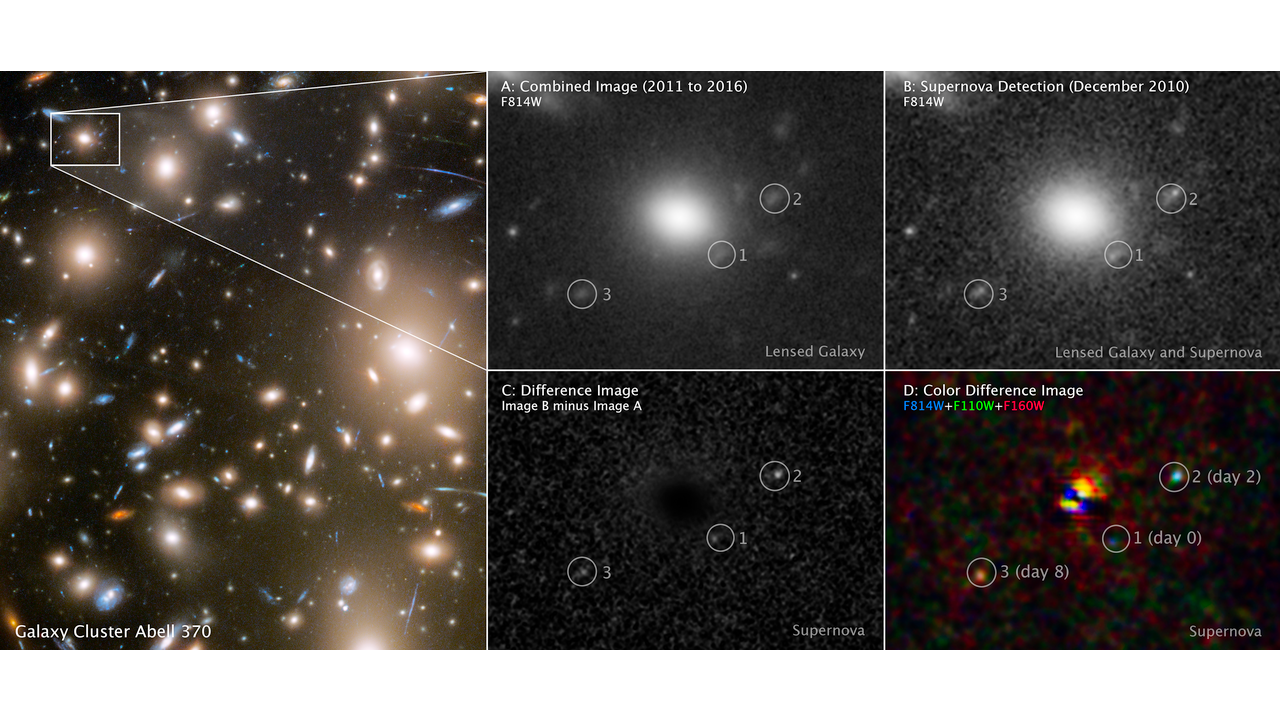
However typically, luck nonetheless performs a task. So it’s with a Hubble picture from 2010, the place the picture occurred to additionally seize a supernova. However, due to gravitational lensing, the only occasion confirmed up at three completely different places inside Hubble’s subject of view. Due to the quirks of how this lensing works, all three of the places captured completely different instances after the star’s explosion, permitting researchers to piece collectively the time course following the supernova, though it had been noticed over a decade earlier.
I’ll want that in triplicate
The brand new work is predicated on a search of the Hubble archives for outdated photographs that occur to seize transient occasions: one thing that is current in some photographs of a location however not others. On this case, the researchers have been looking particularly for occasions that had been gravitationally lensed. These happen when an enormous foreground object distorts area in a means that creates a lensing impact, bending the trail of sunshine originating behind the lens from Earth’s perspective.
As a result of gravitational lenses are nowhere close to as rigorously structured as those we manufacture, they will typically create odd distortions of background objects, or in lots of circumstances amplify it in a number of places. That is what appears to have occurred right here, as there are three distinct photographs of a transient occasion inside Hubble’s subject of view. Different photographs of that area point out that the positioning coincides with a galaxy; an evaluation of the sunshine from that galaxy suggests a redshift indicating that we’re it because it was over 11 billion years in the past.
Given its relative brightness, sudden look, and site inside a galaxy, it is probably that this occasion is a supernova. And, at that distance, lots of the high-energy photons produced in a supernova have been red-shifted right down to the seen space of the spectrum, permitting them to be imaged by Hubble.
To grasp extra concerning the background supernova, the crew labored out how the lens was working. It was created by a galaxy cluster known as Abell 370, and mapping the mass of that cluster allowed them to estimate the properties of the lens it created. The ensuing lens mannequin indicated that there have been really 4 photographs of the galaxy, however one wasn’t magnified sufficient to be seen; the three that have been seen have been magnified by components of 4, six, and eight.
However the mannequin additional indicated that the lensing additionally influenced the timing of the sunshine’s arrival. Gravitational lenses work by forcing gentle to take paths between the supply and observer which have completely different lengths. And, since gentle strikes at a set velocity, these completely different lengths imply that the sunshine takes a special period of time to get right here. Underneath circumstances we’re acquainted with, this finally ends up being an imperceptibly small distinction. However on cosmic scales, it makes a dramatic distinction.
Once more, utilizing the lensing mannequin, the researchers estimated the possible delays. In comparison with the earliest picture, the second earliest had a delay of two.4 days, and the third a delay of seven.7 days, with an uncertainty of a couple of day on all estimates. In different phrases, a single picture of the area produced what was basically a time course of some days.
What was that?
By checking that Hubble knowledge towards completely different lessons of supernovae that we have imaged within the trendy Universe, it was more likely to be produced by the explosion of both a crimson or blue supergiant star. And the detailed properties of the occasion have been a a lot better match to a crimson supergiant, one which was roughly 500 instances the scale of the Solar on the time of its explosion.
The depth of the sunshine at completely different wavelengths offers a sign of the explosion’s temperature. And the earliest picture signifies that it was roughly 100,000 Kelvin, which suggests we have been it simply six hours after it exploded. The newest lensed picture exhibits that the particles had already cooled to 10,000 Okay over the eight days between the 2 completely different photographs.
Clearly, there are newer and nearer supernovae that we will examine in much more element if we need to perceive the processes that drive an enormous star’s explosion. If we’re capable of finding extra of those lensed supernovae within the distant previous, nonetheless, we’ll have the ability to infer issues concerning the inhabitants of stars that have been current a lot earlier within the Universe’s historical past. In the intervening time, nonetheless, that is solely the second we have discovered. The authors of the paper describing it make an effort to attract some inferences, nevertheless it’s clear these could have a better uncertainty.
So, in loads of methods, this does not assist us make main advances in understanding the Universe. However for example of the unusual penalties of the forces that govern the Universe’s habits, it is a fairly spectacular one.
Nature, 2022. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05252-5 (About DOIs).
Go to dialogue…
[ad_2]
Source link


