[ad_1]
The depleting international forex reserve, and the growing authorities borrowing from exterior collectors, might make debt cost in international forex more and more tough for Nepal.
Introduction
To spice up financial actions and obtain greater financial progress, huge funding in infrastructure, technological innovation and improvement, machine studying, synthetic intelligence, human capital, and environmental safety is required. The key sources of funds to finance such investments are taxation and public borrowing. In Least Developed International locations (LDC) like Nepal, there are limitations on elevating income from taxation as a result of low ranges of revenue of individuals, low ranges of financial transactions, and a chance of elevated burden on home financial entities. Subsequently, public debt is seen as a possible choice to finance authorities expenditure and improvement initiatives for which the federal government lacks funds. Right here, public debt is the whole quantity of debt that’s incurred by the federal government to finance and meet its improvement price range.
Determine 1: Estimated Expenditure and Income of Nepal (in NPR Billions)
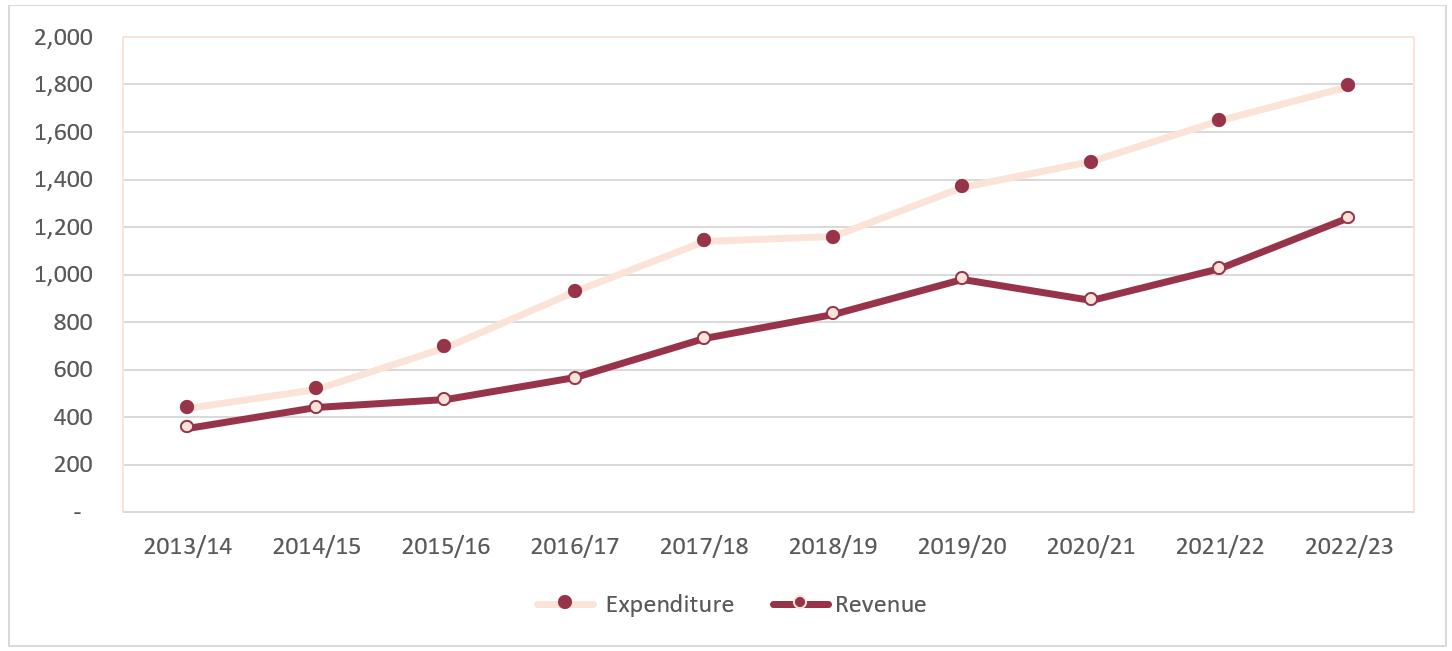
Supply: Funds Speech of respective 12 months from Ministry of Finance
Furthermore, Nepal’s price range deficit, which happens when the bills of the federal government exceed its income, has been progressively growing through the years. In FY 2020/21, the price range deficit as a proportion of GDP was 7.1%. Deficit financing performs an essential position within the yearly price range introduced by the Authorities of Nepal, because it consists of 29.64% of the federal government price range. Yearly, it has been growing by 19.86% on a mean. Determine 1 exhibits a steady and growing fiscal deficit in Nepal, ensuing within the authorities constantly taking mortgage for deficit financing.
Whereas public debt is a vital supply of revenue for the Nepali authorities, and is essential for a growing nation like Nepal, relying closely on borrowing may be pricey and dangerous.
Developments and Present Debt State of affairs in Nepal
Traditionally, Nepal has been borrowing domestically and internationally to satisfy its improvement requirement; the Authorities of Nepal raised its first inside mortgage in 1951, and its first exterior debt in 1963. Exterior mortgage is the very best supply of deficit financing, adopted by inside debt and alter in money reserves, respectively.
Resulting from a rise in expenditure calls for of post-earthquake reconstruction and federalism, authorities borrowing has elevated considerably within the current years. In 5 years to 2020/21, complete public debt elevated by 148%. On the finish of the fourth quarter of the 2021/22, the whole authorities debt reached NPR 2,011.95 billion, out of which exterior debt consisted of NPR 1025.84 billion and inside debt consisted of NPR 986.10 billion. Exterior debt elevated by 5.47% and inside debt elevated by 12.16% as in comparison with third quarter.
The entire debt-to-GDP ratio, which is a metric evaluating nation’s public debt to its complete financial output for the 12 months, offers an outline of how succesful a rustic is in paying its debt. It’s an indicator of how a lot debt a rustic owes and the way a lot it produces to repay its debt. The debt-to-GDP ratio of Nepal on the finish of the fourth quarter of FY 2021/22 was 41.47%, the place exterior debt to GDP ratio was 21.14% and inside debt to GDP ratio was 20.32%. This can be a sharp improve as in comparison with the FY 2018/19, when the whole public debt was estimated to be 30.1% of GDP, out of which exterior debt to GDP ratio was 17% and home debt to GDP ratio was 13.1%.The debt to GDP ratio has exceeded the periodic targets of the Sustainable Improvement Targets and the ultimate 2030 goal of 35%.
Determine 2: Excellent Home Debt and International Debt of the Authorities of Nepal (in NPR Hundreds of thousands)
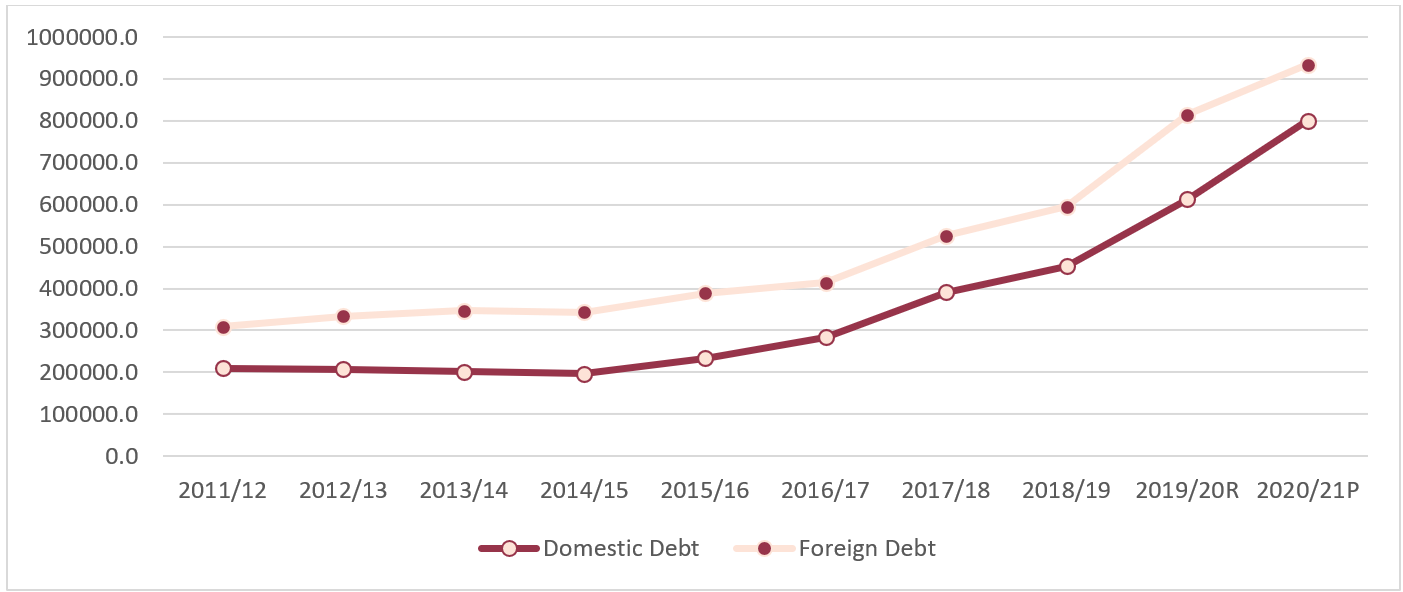
P = Provisional Estimated
R= Revised Estimated
Supply: Present Macroeconomic and Monetary State of affairs Tables Primarily based on Annual information of 2021.22-1 from Nepal Rastra Financial institution
Desk 1: Annual Development Fee of Excellent Debt of Authorities of Nepal
| Yr | Development Fee |
| 2011/12 | 18% |
| 2012/13 | 4% |
| 2013/14 | 2% |
| 2014/15 | -2% |
| 2015/16 | 15% |
| 2016/17 | 12% |
| 2017/18 | 31% |
| 2018/19 | 14% |
| 2019/20R | 36% |
| 2020/21P | 22% |
P = Provisional Estimated
R= Revised Estimated
Supply: Calculated based mostly on NRB’s information on excellent debt of Authorities of Nepal
Over the interval of FY 2011/12 to 2020/21, the general public debt of the Authorities of Nepal has been considerably growing (Determine 2 and Desk 1). Between the FY 2011/12 and FY 2019/20, the Compound Annual Development Fee (CAGR) of public debt of Nepal was 7%. The rationale behind growing public debt of Nepal is the numerous improve within the measurement of price range over time; expenditure of the Authorities of Nepal has been growing, and the expenditure of the federal government being greater than its income (Determine 1).
Implications
Growing public debt is an peculiar drawback for debt administration and poses a problem for the financial system. A examine on the impact of public debt on Nepal’s financial progress found that authorities borrowing has largely been funded on unproductive sectors, ensuing within the authorities’s lack of cash and having to take out an extra new mortgage to repay the outdated loans. Additional, this has resulted in a rise within the complete excellent public debt and its curiosity however no enchancment within the debt compensation potential.
Furthermore, whereas the nation is borrowing extra for deficit financing, a big portion of the federal government’s price range is getting used for debt principal compensation and curiosity cost. Whereas the federal government estimated to earn NPR 1.24 trillion in revenues in FY 2022/23, it plans to pay 15% of its estimated income to international and home collectors. General, this negatively impacts the federal government’s capability to finance improvement actions inside the nation.
It is usually essential to research the debt state of affairs of the nation close to the international alternate reserve. A rustic must pay of its exterior debt with its international alternate reserve. Whereas exterior loans are cheaper than home loans, exterior loans carry threat of international alternate fluctuations. The debt legal responsibility in home forex phrases of Nepal is on the rise on account of depreciation of the Nepali rupee towards the US {dollars}. The excellent debt-to-foreign alternate ratio, which was 26% in 2016/17, elevated to 57% in 2020/21[1]. The depleting international forex reserve, and the growing authorities borrowing from exterior collectors, might make debt cost in international forex more and more tough. This might push the nation into the vicious cycle of borrowing extra to repay the prevailing exterior debt.
Conclusion
Presently, the federal government has taken many steps to lower borrowing and improve international reserve alternate of the nation. As an example, to curb the rising debt, the not too long ago enacted Public Debt Administration Act has capped exterior debt at one-third of the earlier fiscal 12 months’s GDP. Furthermore, with the brand new regulation, the federal government can elevate a most inside mortgage of NPR 256 billion for the present FY 2022/23. These insurance policies are anticipated to discourage the federal government from borrowing recklessly and encourage it to make well timed debt funds so as to have the ability to borrow extra.
Along with introducing insurance policies to assist cut back the Authorities of Nepal’s debt, the nation must additionally use the borrowed cash successfully. Presently, borrowing has largely been utilized on unproductive sectors. To have the ability to repay the loans in the long run, the Authorities of Nepal ought to use the borrowed cash to create a sustainable financial system by investing in productive sectors with excessive ranges of effectivity. That is particularly extra related now as Nepal is getting ready to graduate from the LDC group in 2026, on account of which Nepal might lose its advantages of decrease price of pursuits. Subsequently, to keep away from additional growing Nepal’s debt burden after LDC commencement, the nation ought to strategize and use the borrowed cash extra effectively.
…
[1] Primarily based on calculation from preliminary information on international debt and gross foreign exchange reserve offered by NRB
[ad_2]
Source link

