[ad_1]
Guidelines for franchising in Indonesia had been first revealed in 1997 by a authorities regulation and a ministerial decree, which was subsequently amended a number of occasions. The franchising rules presently in impact are Authorities Regulation No. 42 of 2007 regarding Franchises and Regulation issued by the Minister of Commerce No. 71 of 2019 in regards to the Implementation of Franchising (MOT No. 71 of 2019).
Franchises in Indonesia should meet sure standards that distinguish them from different forms of companies, and franchising should be primarily based on a franchise settlement ruled by Indonesian legislation. Previous to coming into right into a franchise settlement, a franchisor should present a prospectus (disclosure doc) to the possible franchisee a minimum of two weeks earlier than the execution of the franchise settlement in order that the possible franchisee has ample time to overview the status and goodwill of the franchisor by the prospectus. The prospectus should comprise numerous particulars in regards to the franchise enterprise, its administration, its operations, and different related elements.
Each native and international franchisors should get hold of a franchise registration certificates—known as an STPW—from the Ministry of Commerce earlier than providing their franchises to potential franchisees. The franchisee can also be required to acquire an STPW. The STPW for the franchisor is the proof of prospectus registration, whereas the STPW for the franchisee is the proof of registration of the franchise settlement. Franchisors and franchisees who’ve STPWs are required to submit experiences on franchise enterprise actions to the Ministry of Commerce’s director of enterprise growth and distribution by the tip of June annually.
As much as three written warnings might be served on a franchisor or franchisee who doesn’t adjust to the registration necessities. A fantastic of as much as IDR 100 million (approx. USD 6,400) might be imposed if the franchisor or franchisee fails to answer the warnings.
MOT No. 71 of 2019 on franchising was a step ahead for the business, because it streamlined some steps and relaxed among the extra onerous necessities. The desk beneath signifies how some typical franchising issues in Indonesia are dealt with underneath the present rules.
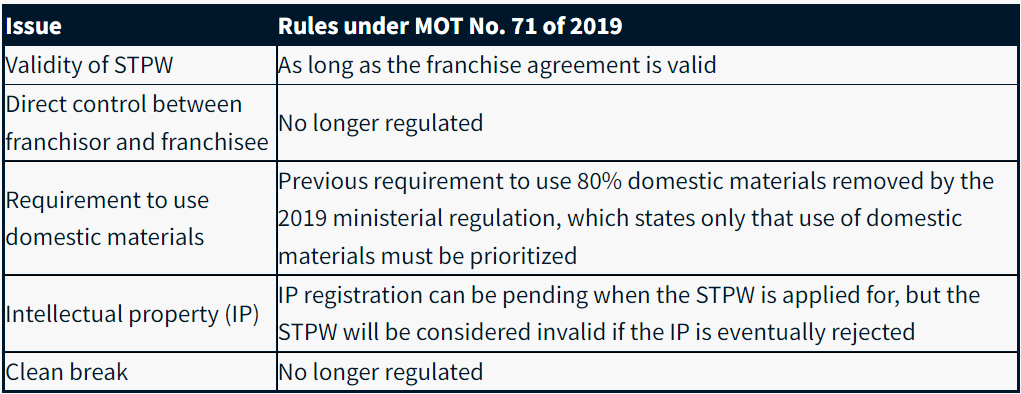
Franchising in Relation to Competitors and Antitrust Legislation
Indonesia’s Legislation No. 5 of 1999 in regards to the Prohibition of Monopolistic Practices and Unfair Enterprise Competitors prohibits:
- restrictive agreements and practices, together with oligopoly, monopoly, coming into into cartels, worth discrimination, and resale worth upkeep;
- abuse of dominance;
- mergers, amalgamations, or acquisitions of firms that can lead to monopolistic practices or unfair enterprise competitors; and
- conglomerate energy by interlocking directorates or majority fairness stakes in a number of firms accounting for a market share exceeding 50%.
The legislation particularly mentions franchising, exempting franchise agreements from its checklist of prohibited agreements. That is supposed to learn holders of IP rights; normally, if the contents of the settlement are supposed to guard IP rights or keep the traits of the IP rights used within the franchise, the settlement will be exempted from Legislation No. 5 of 1999.
[ad_2]
Source link


