[ad_1]
Nepal’s digital innovation ecosystem is at a nascent stage; nevertheless, it is among the fastest-growing industries. ICT service exports have been price over NPR 1.9 billion in FY 2021/22 in comparison with simply over NPR 540 million in FY 2019/20 and NPR 760 million in FY 2020/21. Latest years have seen an increase within the variety of IT-enabled companies, because of a growing ecosystem of digital entrepreneurship. A brand new technology of home IT service suppliers has emerged who provide progressive and specialised options to a number of native calls for.
Nepal’s rising startups have developed digital merchandise which have eased the lives of Nepalis over the previous many years – by means of accessible schooling, ride-sharing platforms, automated HR techniques, well being techniques, monetary apps, meals companies, logistics and help companies, amongst others. Homegrown e-commerce, digital companies, logistics, fee platforms, and cellular wallets have turned out to turn into large success tales in Nepal’s tech house. Nonetheless, regardless of the rising ICT sector, native IT companies are perpetually confronted with a spread of advanced points that impression efficient operations and progress alternatives for the sector.
Among the key obstacles to innovation are highlighted beneath:
Determine 1: Obstacles to Native Digital Innovation in Nepal
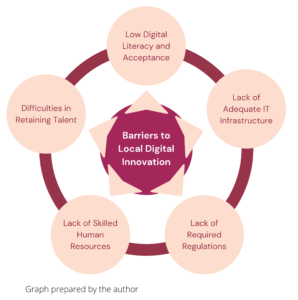
- Lack of Required Laws
As a result of unclear or outdated laws, progressive tech startups wrestle to adjust to the legislation. When IT firms attempt to register their firm with the federal government, they steadily uncover that there isn’t any particular class that accommodates them. The Nepal Customary Business Classification (NSIC) categorizes most IT-related companies into “programming”, “pc consulting”, “internet portals” and different “IT and pc service actions”. Not one of the legal guidelines in Nepal clearly outline startup, which creates additional ambiguity. Entrepreneurs are steadily discouraged from taking possibilities and implementing progressive concepts attributable to a scarcity of supportive insurance policies for tech-based firms. The Authorities of Nepal drafted an e-commerce invoice virtually two years in the past, nevertheless, progress on the invoice is unknown.
Equally, the outdated transportation legislation in Nepal, which just about forbids non-public vehicles from for-profit actions, makes it troublesome for ride-sharing startups to operate. As an example, ride-sharing companies like Pathao and Tootle fall beneath the current regulatory framework’s definition of an internet retailer or web site, and so they have been going through challenges in complying with the foundations. Moreover, the federal government has not but outlined its regulatory and coverage stances on cutting-edge expertise like synthetic intelligence (AI) and the web of issues (IoT). One of these delay will inevitably hinder the innovation and progress of tech companies.
Whereas lawmakers have vowed to create new rules to encourage expertise within the numerous financial sectors, there was little to no motion as of right now. The federal government should purchase the political will, information, and motivation wanted to reform rules in a method that might encourage non-public sector improvement within the digital trade. Moreover, the federal government ought to prioritize interventions for e-commerce and different ICT merchandise as quickly as potential when it comes to regulatory necessities whereas additionally formulating rules to encourage better Funding within the regional IT sector.
- Lack of Expert Human Assets
For startups in Nepal, increasing is close to unattainable owing to a scarcity of certified technical and mid-level managers. Equally, retaining expertise is among the hardest challenges. As a result of subpar high quality {of professional} coaching and tech schooling, many companies find yourself spending months investing in new-hire coaching. Solely round 7,500 college students take up IT-related programs annually and yearly, round 5,500 graduate from IT faculties in Nepal. Out of this, merely 20% be part of the IT trade in Nepal whereas the remainder both transfer overseas or select completely different profession paths. Even out of the 20% who stay within the trade, solely a restricted variety of technicians are prepared to begin new ventures or be part of native tech companies. The excessive fee of migration of expert staff additionally reduces the provision of certified managers and technicians. Since few graduates keep within the workforce lengthy sufficient to advance to center administration, companies should actively put money into attracting and coaching graduates. This has confirmed to be one of many largest challenges for Nepali tech companies.
Subsequently, this can be very necessary to reinforce skill-building packages. The non-public sector and the federal government must work collectively to replace the IT curriculum to higher replicate trade calls for. Equally, the growth of extra enterprise incubators and boot camps may additionally assist IT firms and assets turn into extra succesful. The hole within the prime degree will also be fulfilled if the federal government permits the hiring of gifted foreigners in Nepali companies.
- Difficulties in Retaining Expertise
Native Nepali IT firms offering services and products to the home market discover it extraordinarily troublesome to retain good staff. Whereas migration is among the causes firms have a tough time retaining expertise, the rising Enterprise Course of Outsourcing (BPO) trade in Nepal is one other main motive that has put the vast majority of Nepali tech firms in an existential disaster. In essence, market forces discourage tech professionals from providing companies for prices which can be decrease than what they obtain for outsourcing jobs. The costs that BPOs are prepared to pay for recruiting are increased than what the native tech market in Nepal can bear. This wage-rate hole has created each disincentive for Nepali tech experience to service native clientele, leading to native service-providing IT companies both not getting the required assets or having assets depart to affix BPOs. Subsequently, those that don’t outsource are liable to vanishing from existence.
Expert assets can’t be stopped from leaving for better-paying alternatives. Nonetheless, to retain such staff, native firms can create a beautiful work tradition that creates alternatives for workers to develop and develop. Equally, with an growing variety of Non-public Fairness and Enterprise Capital companies, together with the influx of funding from improvement companies, alternatives for native IT firms to entry capital would additionally enhance. This might assist the businesses pay good cash for his or her assets.
- Lack of Sufficient IT Infrastructure
The weak IT infrastructure and absence of high-calibre IT parks in Nepal have additionally had an impression on the expansion of Nepal’s IT trade. The one area with enough infrastructure is Kathmandu valley, the place the vast majority of IT firms are positioned. Second, the demand for family IT companies is constrained by the low broadband penetration fee and the subpar high quality and worth of cellular web. Specialised expertise parks might help constrained areas to amass enough technological and infrastructure capability. Nonetheless, the lone government-run IT Park in Nepal has had problem drawing enterprise principally due to the insufficient infrastructure. The federal government can overcome the issue of getting insufficient IT infrastructure, and Enhance and modernize the present IT Park with extra non-public sector involvement.
- Lack of Sufficient Digital Literacy and Acceptance
Whereas the usage of digital fee techniques has skyrocketed in recent times, the usage of such channels for fee of products purchased on-line continues to be restricted and money continues to be the popular technique of fee for Nepali on-line patrons. Equally, the digital divide between the city and rural populations is a major problem for increasing the acceptance of digital services and products. Native tech firms, due to this fact, face challenges whereas increasing as they’re compelled to put money into digital consciousness as nicely, other than specializing in growing and advertising and marketing their merchandise. Until the acceptance of digital merchandise and literacy doesn’t enhance in main components of the nation, native digital firms would have a tough time increasing their market.
Method Ahead
On condition that home IT suppliers have a robust capability to affect the market, it’s essential to contemplate their potential. The digital economic system in Nepal has been rising quickly, however points like inefficient market techniques, a scarcity of human capital, a scarcity of related insurance policies and the nation’s widespread digital disconnectivity are hindering the event of native digital firms. It’s essential to give attention to the growth of digital infrastructure, digital literacy, and coaching alternatives outdoors the Kathmandu valley.
[ad_2]
Source link


