[ad_1]
January 4, 2023
Jordanians are protesting once more. It’s time for financial and administrative reforms.
On December 14, 2022, a brand new nationwide strike came about in Jordan 4 years after one other strike toppled the federal government of Prime Minister Hani Mulki. Once more, the motives are financial. Led by truck drivers, the brand new protests in Jordan are over the rise in gasoline costs following the federal government’s disclosure of its deliberate finances for 2023. For the reason that strikes started, the protesters loved a big stage of help amongst Jordanians, who’re already affected by the present financial state of affairs, particularly with the rise of unemployment and poverty charges.
The protests led to clashes with police and the killing of a police officer on December 16, 2022. The state of affairs in Jordan raises many questions on why Amman remains to be unable to reform its financial system regardless of receiving super quantities of international assist—round $3.5 billion yearly. It additionally raises many questions on why the Jordanian authorities seeks simple options, like gasoline worth will increase, as an alternative of implementing structural reforms to unravel Jordan’s fiscal and financial points.
Within the Jordanian context, worldwide and native analysts blame this case on restricted assets, restricted fiscal capability, and regional turmoil. Nevertheless, these are solely signs of Jordanian financial structural weaknesses.
High assist recipient however sluggish on reform
Jordan is very assist dependent and among the many high US and worldwide international assist recipients globally. Regardless of that, international assist was one among Jordan’s principal stabilizing elements prior to now few years. But, many questions are being raised amongst Jordanians and worldwide observers concerning sluggish reform implementation within the nation and the persistently weak financial system. In truth, Jordan is among the high international assist recipients globally. For instance, Jordan was the second highest aid-receiving nation from the US in 2021. In keeping with the Organisation for Financial Co-operation and Improvement (OECD) information, Jordan obtained round $32.4 billion throughout 2011-2020 in international assist, as proven within the graph beneath.
However the super quantities of international assist obtained by Jordan, the nation is at present affected by a 22.6 % general unemployment charge, a public debt constituting round 110 % of the nation’s GDP, and round 27 % of the inhabitants residing in poverty. Furthermore, polling information reveals a big stage of dissatisfaction amongst Jordanians, the place 70 % imagine that their nation is “ruled within the curiosity of some.” Nevertheless, as this text argues, that isn’t the one difficulty, with there being 5 principal obstacles to financial reform implementation in Jordan.
Lack of presidency autonomy
Civilian authorities autonomy vis-à-vis different forces inside a political system is a defining issue of a authorities’s capability to implement reform. Within the Jordanian context, the federal government faces a number of forces that undermine its capability to manage state establishments and take possession of reform implementation. For instance, the monarch of Jordan enjoys in depth constitutional powers leaving restricted room for his civilian authorities’s management and lead of state establishments.
Throughout 2016 and 2022, the Jordanian structure was amended to broaden the monarch’s powers to the judiciary, international coverage, protection, and safety, alongside his powers of hiring and firing the ministerial cupboard, hiring the home of senate, and dissolving the parliament. The structure now grants the king the powers of appointing and dismissing the chief justice, head of the sharia judicial council, grand mufti, chief of the royal court docket, minister of the court docket, and court docket advisors.
This growth of the king’s powers has been related to an elevated turnover of ministerial cupboards. From 1999 till the current, Jordan has had 13 prime ministers, nineteen completely different governments, and forty-two cupboard reshuffles. This led to short-aged governments with a median life span of 1.2 years. The excessive turnover made Jordanian ministerial cupboards hesitant to take unpopular measures which may contradict the royal court docket imaginative and prescient—lest they be dissolved by the king.
Equally, because of the weak financial system, Jordanian governments have restricted house to implement essential reforms that spawn controversy and public dissent. The amassed public grievances, weak financial state of affairs, and the massive penetration of social media made it simpler for Jordanians to assemble and specific their anger in opposition to authorities insurance policies. Consequently, this has led to governments delaying reforms or diverting insurance policies.
Jordanians don’t belief their political system
A current 2022 nationwide survey printed by the Worldwide Republican Institute in Jordan reveals that nearly 40 % of Jordanians imagine the nation is generally headed within the incorrect route, a 24 % improve from 2020. Equally, public belief ranges within the authorities—significantly the ministerial cupboard—have declined considerably after the 2011 Arab Spring. The Arab Barometer information reveals that the proportion of Jordanians who belief the federal government declined from 71.5 % in 2011 to 43.3 % in 2020. The identical applies to parliament, the place belief ranges declined from 48 % in 2011 to 13.7 % in 2018. This decline in social belief in state establishments diminished the credibility of present reform applications and created more room for populist forces to construct affect that hinders reform.
Poor elite recruitment mechanisms
With the persistence of “institutional favoritism,” Jordan lacks clear, clear, and efficient elite recruitment mechanisms. Public workplaces are obtained by way of favoritism, nepotism, and clientelism. In different phrases, “elite recruitment continues to be based mostly on private friendship, if not household relationship,” in keeping with teachers Oliver Schlumberger and André Financial institution.
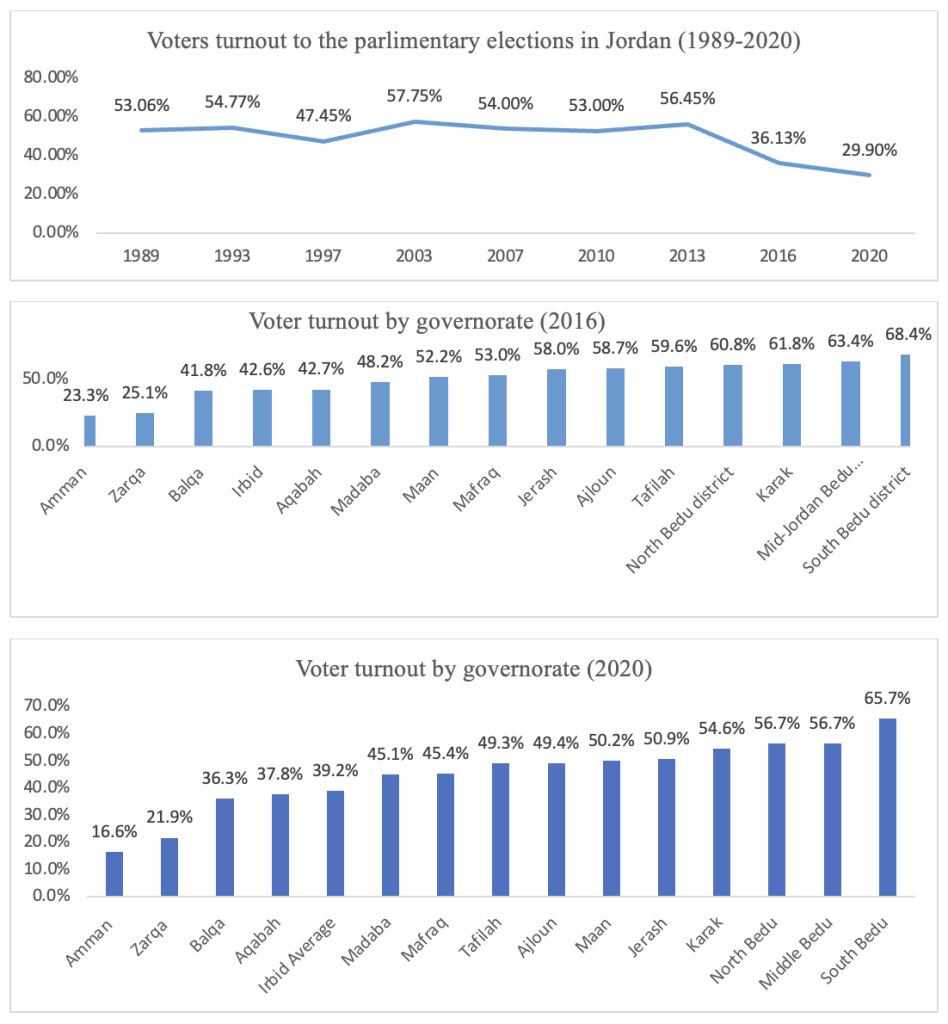
In relation to elected officers, Jordanian parliaments face many legitimacy questions as a consequence of unfair illustration of the general public. For example, voter turnout within the newest elections of 2020 reached solely 29.9 %, with many questions raised on election equity as a consequence of COVID-19 measures again then. Furthermore, voting conduct in Jordan is predominantly tribal.
Within the 2016 and 2020 parliamentary elections, the vast majority of voting got here from tribal districts, whereas the city cities of Amman and Zarqa witnessed the bottom voter turnout in each elections (within the 2020 elections, eligible voters in Amman and Zarqa constituted 53.54 % of the nationwide voters). On the opposite aspect, the best turnout charges in each elections got here from the three Bedouin districts of Jordan, along with different cities with tribal majorities, as proven within the graphs beneath.
Non-public sector marginalization
Regardless of Jordan’s lively involvement in liberalization applications with the World Financial institution and Worldwide Financial Fund since 1989, the Jordanian personal sector nonetheless struggles with governmental management over the financial system. In truth, investor confidence ranges have been declining over the previous few years. The Investor Confidence Survey printed by the Jordan Technique Discussion board reveals that the share of traders who see the enterprise setting being “not encouraging” for funding elevated from 56 % in 2017 to 68.4 % in 2022.
Furthermore, the Jordanian personal sector is very state-dependent, making it much less capable of develop autonomously. For instance, monetary services—corresponding to loans and authorities bonds—supplied by the Jordanian banking sector to the Authorities of Jordan constituted round 22.7 % of the sector property through the interval 2010-2020, making the sector extremely depending on the state and fewer capable of present financing for the personal sector. Equally, the Jordanian authorities is at present doing enterprise by means of the army. In keeping with the Jordanian ministry of commerce and trade information, seventeen new corporations had been registered throughout 2006-2022 with the Jordanian Armed Forces (JAF) as a associate. Eleven of those corporations had been registered between 2019 and 2022. These companies owned by the Jordanian army work in army gear improvement, agriculture, mining, development, actual property, and telecommunications. Due to this fact, the federal government of Jordan is crowding the personal sector as an alternative of making a growth-enabling setting for personal enterprises.
Declining human capital
The excessive unemployment charge in Jordan (22.6 %) is attributable to many structural distortions within the labor market. Considered one of these principal issues is declining human capital. Jordan’s rating of 55/100 within the World Financial institution’s 2022 human capital index is “decrease than the common for the Center East [and] North Africa area.” This suggests that “a toddler born in Jordan simply earlier than the pandemic can be 55 % as productive when she grows up as she may very well be if she loved full training and full well being.” Moreover, Jordanian college college students scored beneath the worldwide common on the 2018 Programme for Worldwide Pupil Evaluation (PISA) check. In different phrases, Jordan can not fill the personal and public sectors with proficient and progressive employees.
Primarily based on the aforementioned points, Jordan’s financial struggles can’t be diminished to the regional state of affairs and weak fiscal capability. Many different structural points should be tackled by severe financial and administrative reforms that require management and political will. The present reform plans neglect the basics and suggest superficial financial reforms.
Politically, the present plans attempt to construct an ineffective democratic façade. With out tackling the basis causes of the nation’s points, corresponding to corruption, weak training, favoritism, political tribalism, and lack of management, the nation will solely delay the disaster and it’ll snowball into one thing bigger sooner or later. Due to this fact, Jordan is anticipated to witness extra protests and public dissent if structural reforms are usually not carried out.
Laith Alajlouni is a Jordanian political economist. He labored as a coverage advisor for various organizations together with the World Financial institution. Observe him on Twitter: @LaithAlajlouni.
Additional studying
Picture: A bike owner passes in entrance of the picture of Abdullah II of Jordan, contained in the Amman Citadel historic web site.
On Wednesday, January 30, 2019, in Amman, Jordan. (Photograph by Artur Widak/NurPhoto)
[ad_2]
Source link


