[ad_1]
To realize a sustainable e-Governance construction, Nepal must deal with key areas comparable to enhancing its digital infrastructure and selling digital literacy amongst its residents.
‘Digital Governance’ or what’s often referred to as e-Governance, makes use of data and communication applied sciences (ICTs) comparable to huge space networks, the web, and cellular computing at numerous ranges of presidency and the general public sector to boost governance. Nonetheless, e-Governance and e-Authorities are phrases that usually trigger confusion. “e-Authorities” is a system that makes use of ICT to boost authorities operations and procedures with the aim of boosting civic engagement and effectiveness, whereas e-Governance refers back to the performance that makes use of ICT to boost a variety and high quality of providers delivered to the residents.
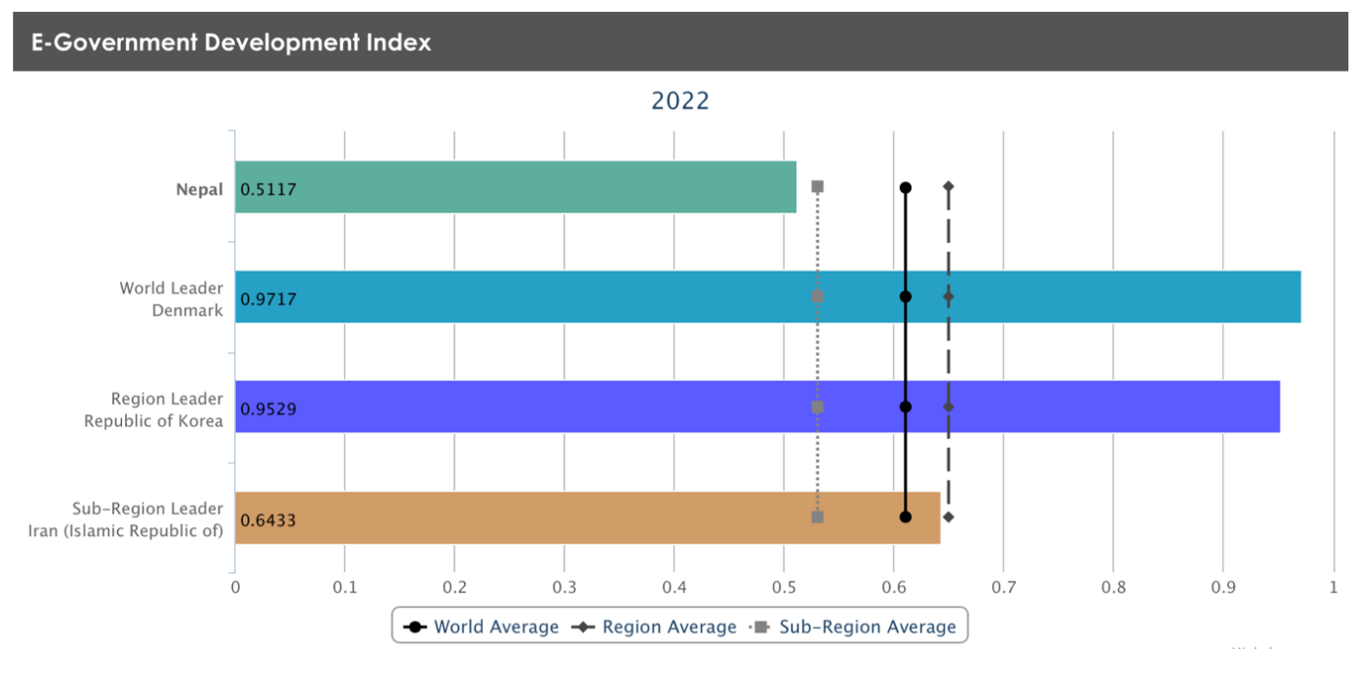
The primary e-Governance initiative was launched in Chile in 1972. At present, there are 193 member states listed within the e-Authorities Improvement Index (EDGI) of the UN, which evaluates the nationwide web sites, and the effectiveness of the e-Authorities insurance policies and techniques within the supply of important providers of the member states. Nepal at the moment ranks 125 out of 193 member states with a rating of solely 0.5117 out of 1, which continues to be low in comparison with the main nations (Figures 1 and a couple of).
Determine 1: EDGI rank of Nepal in contrast with main nations
Supply: United Nations
Determine 2: 12 months-wise EDGI worth and Nepal’s Rank

Supply: United Nations
The Authorities of Nepal has acknowledged the significance of the ICT sector and has made clear efforts to ascertain e-Governance within the nation for the reason that introduction of the IT Coverage of 2000. Though the infrastructure in Nepal is underdeveloped or inconsistently developed, numerous stakeholders have acknowledged the potential to boost the nation’s improvement by way of e-Governance.
Interruptions to higher service supply
Whereas Nepal’s efforts and developments within the sphere of e-Governance are a step in the proper path there are nonetheless areas that require extra consideration and enchancment for higher service supply.
Authorities’s Strategy to e-Governance
The Digital Nepal Framework (DNF), launched in 2019, supplies a complete roadmap for strengthening the e-Governance panorama of Nepal. The framework acknowledges that constructing a powerful digital governance system requires leveraging current initiatives comparable to the federal government Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), Nationwide Id Card, and automation of significant registration and land registration processes. Though there was some progress within the nation, the E-Authorities masterplan continues to be within the draft section and there are considerations about interoperability. Moreover, there’s a want for regulatory measures to be put in place to ascertain a transparent authorized framework for e-Governance The nation has made progress in growing its ICT insurance policies, which signifies a level of political dedication. Nonetheless, political instability and a scarcity of management, dedication, and coordination are three main obstacles to e-Governance implementation in Nepal. There are additionally points comparable to frequent transfers of officers and a scarcity of coordination between authorities businesses as a consequence of differing political pursuits.
The shortfall of certified workforce
One of many vital challenges confronted in strengthening the e-Governance panorama of Nepal is the scarcity of expert human labor. Whereas not all literate Nepalis converse English, the absence of software program of their native language poses a substantial drawback. Moreover, the low literacy price, 71% as of 2021, within the nation has led to a shortage of expert human sources within the area of ICT. Nonetheless, expert ICT labor shouldn’t be fully non-existent in Nepal. Whereas a standalone ICT training plan was solely printed in 2013, 4 universities had been already offering ICT training in Nepal as early as 2002. Regardless of this, there is a matter with the older era missing any ICT abilities, and brain-drain is seeing IT college students go for overseas training and jobs, which additional exacerbates the scarcity of human sources within the area of ICT in Nepal. The general public’s publicity to expertise has elevated their expectations from the native degree, however there are nonetheless points with native integration for e-Governance. Moreover, the shortage of fundamental pc data amongst nationally chosen authorities personnel has resulted in reluctance in the direction of utilizing expertise, which should be addressed to make sure the success of e-Governance initiatives in Nepal.
Constraints in delivering public providers
The Authorities of Nepal has launched e-Governance to enhance the administration of presidency providers and the connection between public servants and the broader society. The federal government launched the Nagarik App to streamline service supply, nevertheless it fell wanting its goal to combine 60 providers by 2021/22, as solely 45 providers have been built-in to date. Moreover, challenges comparable to lack of curiosity and dedication from all three tiers of the federal government, restricted funding, inadequate useful resource mobilization, ineffective ICT insurance policies, and incapability to enhance ICT capability have made the method of receiving authorities providers tedious for residents. Regardless of the institution of on-line registration methods for providers like sensible driving licenses, Nationwide IDs, and e-passports, shoppers nonetheless have to attend in lengthy strains and use middlemen to get their work executed in workplaces easily. Moreover, residents have to attend for over a 12 months to get their sensible licenses and Nationwide IDs made after making use of.
Inequitable within the distribution of expertise
Digital connectivity has been rising exponentially through the years with over 1.97 million households having web subscriptions. Nonetheless, lack of affordability, digital literacy, and entry to a digital system nonetheless tends to place folks at a drawback when it comes to gaining access to these providers. Moreover, those that are already deprived are inclined to belong to teams in society with decrease ranges of entry. Entry to authorities data and providers can be essential for such teams. Nonetheless, in accordance with the World Financial institution Handbook on e-Authorities for growing nations, they might not profit from enhancements to service high quality and better alternative by way of on-line providers. The existence of e-Authorities providers might encourage folks to entry the web. Nonetheless, for many residents, interacting with the federal government on-line is rare and never usually the first motive for households to buy a private pc and web connection.
Impediments to upholding information and cybersecurity
With the web changing into more and more prevalent and the rise of data-driven practices, the federal government has been amassing residents’ information, together with private particulars and biometric data, for numerous functions comparable to nationwide identification, voter playing cards, and passports. Regardless of the federal government’s obvious funding in buying IT infrastructure, there appears to be a scarcity of precedence from their aspect on capability constructing, coaching, and hiring expert information scientists. Nepal’s patchy cybersecurity report, and the latest Aadhar information breach in India, pose a query in regards to the safety of nationwide ID card information. Actually, on the Tribhuvan Worldwide Airport, technical and system points, have ceaselessly interrupted immigration providers, inflicting inconvenience to passengers and impacting worldwide flights.
Manner ahead
To realize a sustainable e-Governance construction, Nepal must deal with key areas comparable to enhancing its digital infrastructure and selling digital literacy amongst its residents. The federal government ought to prioritize training about e-Authorities providers to extend consciousness and utilization of accessible providers. The personal sector can play a major position in growing and implementing e-Authorities providers. Due to this fact, private-public partnerships, aside from the Nationwide Telecommunications Authority’s Rural Telecommunications Improvement Fund (RTDF), needs to be promoted to speed up e-Authorities improvement. Particularly, Nepal ought to deal with growing a Nationwide Single Window and e-Customs system to streamline commerce and enhance authorities service supply. Moreover, partnering with South Korea for e-Governance can result in substantial advantages for Nepal when it comes to expertise switch and capability constructing. Nonetheless, any e-Governance initiative should be citizen-inclusive and make use of a bottom-up strategy to make sure that the providers delivered cater to the wants of the folks. This requires lively engagement and participation of residents within the planning, implementation, and analysis of e-Authorities packages to make sure that their wants and preferences are taken under consideration.
[ad_2]
Source link


