[ad_1]
Originally of the present fiscal yr 2022/23, the federal government had set an bold goal of 8% financial progress. Nonetheless, when the financial system sputtered, actuality set in, and throughout the finances’s midterm evaluate, the expansion forecast was lower in half, arriving at 4%. On Might 2, 2023, the Nationwide Statistics Workplace (NSO) launched the Nationwide Accounts Statistics, revealing a dismal state of Nepal’s financial system. The Gross Home Product (GDP) progress charge at present costs for FY 2022/23 was estimated at 1.87%. That is the bottom since FY 2015/16 when it was at 0.43% following the earthquake and for the reason that destructive progress of -2.37% in FY 2019/20 brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic. Likewise, this projection is far lower than the 4.1% progress charge which was estimated by the World Financial institution and the Asian Improvement Financial institution (ADB). Based mostly on the NSO’s forecast, Nepal’s GDP in 2022/23 is projected at NPR 5,381 billion (USD 41.18 billion). Likewise, the per capita GDP stood unchanged at USD 1399.
Determine 1: Nepal’s GDP Progress Fee at Present Costs
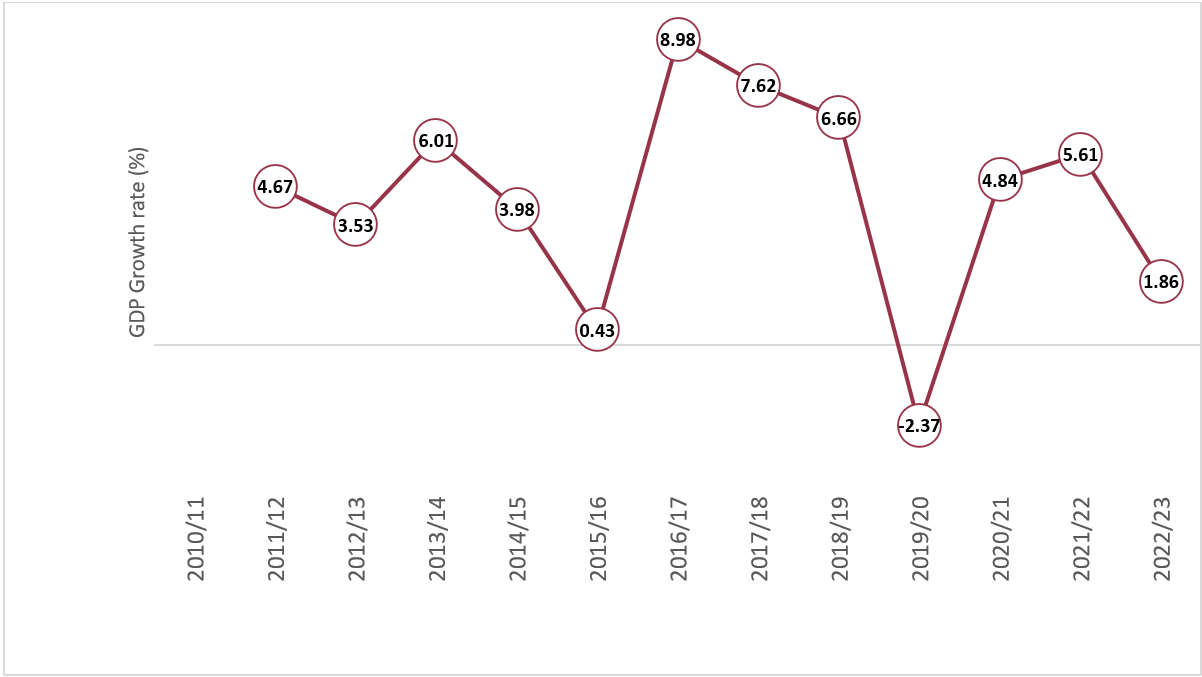
Supply: NSO (2023)
Progress and Composition of Nepal’s Financial Sectors
As per the nationwide accounts statistics, the first sector, i.e., agriculture is estimated to develop at a charge of two.69% in FY 2022/23, a slight improve from 2.39% the earlier yr. In the meantime, the expansion of the secondary sector i.e., manufacturing, which was 10.89% in FY 2021/22, is predicted to droop to a mere 0.56% in FY 2022/23. Likewise, the tertiary or service sector is estimated to fall from 5.32% in 2022/23 to 2.33% in 2022/23. When it comes to the financial sectors’ composition, the first sector’s contribution to GDP is anticipated to be 24.6%, barely decrease than the earlier yr’s 25.2%. The secondary sector’s contribution is projected to lower from 13.5% to 12.9% in 2022/23, whereas the service sector’s contribution is estimated to extend from 61.2% to 62.4%.
Determine 2: Progress of Financial Sectors at Primary Worth
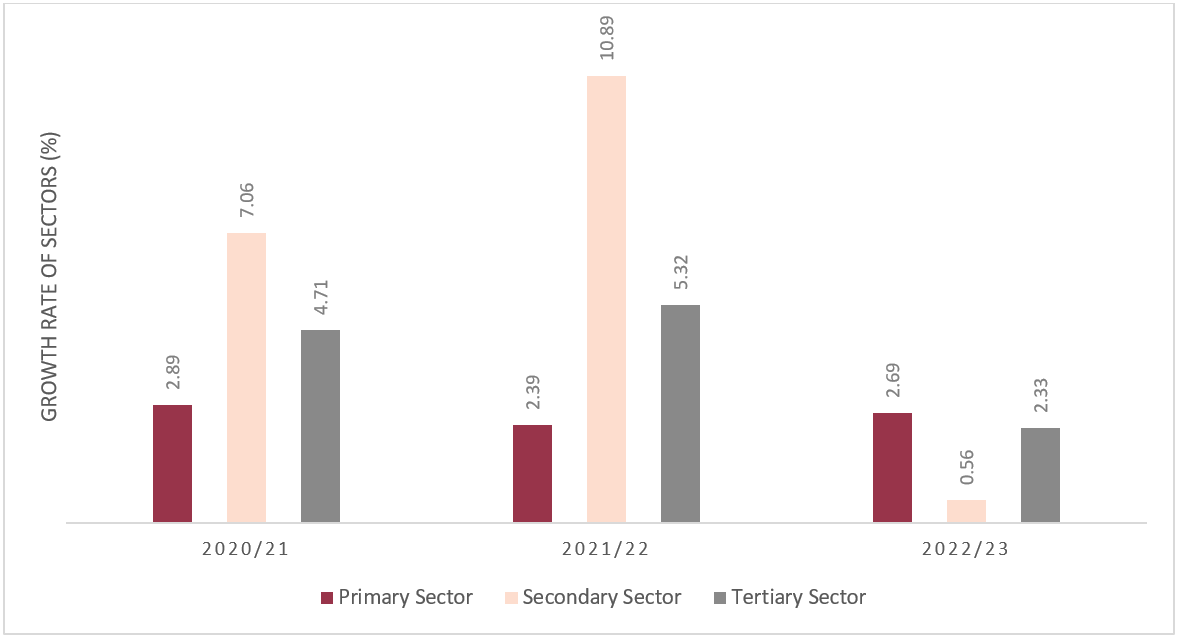
Supply: NSO (2023)
Determine 3: Composition of Financial Sectors in GDP at Present Costs
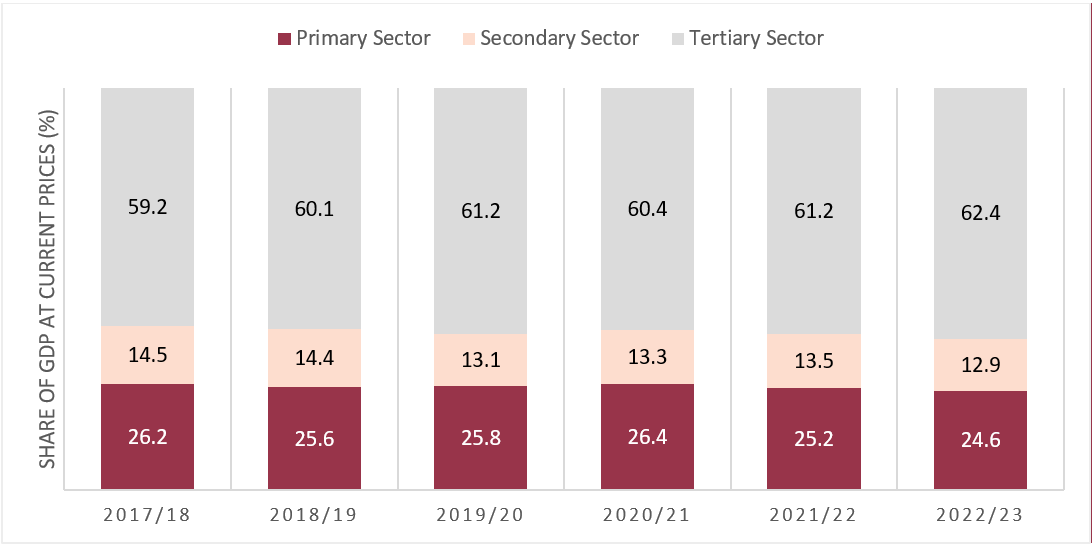
Supply: NSO (2023)
The Downturn of Nepal’s Main Financial Sectors
The slowdown in Nepal’s manufacturing, wholesale, and retail commerce, transportation, mining, building, and different sectors slowed this yr’s total financial progress. Compared to a progress of 8.84% in FY 2021/22, the NSO forecasted that the mining sector would solely develop by a modest 1.11% in FY 2022/23. Building spending, which elevated by 7.08% within the earlier fiscal yr, is predicted to say no by 2.62% this yr. Equally, in comparison with a progress of seven.46% within the earlier fiscal yr, the wholesale and retail commerce sector, which contributes 15.39% to the nation’s GDP, is forecasted to nose-dive by a destructive 2.96% this fiscal yr. Likewise, the expansion of the manufacturing sector is anticipated to decelerate by -2.04% in FY 2022–2023 as per the NSO. However, the vitality and tourism/hospitality sectors are predicted to expertise an enormous bounce in FY 2022/23. The hospitality sector comprising lodging and meals companies, which benefited from a sluggish however regular revival within the tourism trade and an increase in customer numbers, is estimated to rise by 18.56%. Likewise, the vitality trade, because of the improve within the manufacturing capability of hydropower crops, is predicted to develop by 19.36%.
Desk 1: Contribution and Progress Fee Forecast of Industries in 2022/23
| Industrial Classification | Contribution to GDP (%) | Progress Fee (%) |
| Agriculture, forestry, and fishing | 24.12 | 2.73 |
| Mining and quarrying | 0.51 | 1.11 |
| Manufacturing | 5.32 | -2.04 |
| Electrical energy, fuel, steam, and air-con provide | 1.64 | 19.36 |
| Water provide; sewerage, waste administration, and remediation actions | 0.46 | 2.16 |
| Building | 5.52 | -2.62 |
| Wholesale and retail commerce; restore of motor automobiles and bikes | 15.39 | -2.96 |
| Transportation and storage | 6.79 | 1.14 |
| Lodging and meals service actions | 1.98 | 18.56 |
| Data and communication | 1.97 | 4.07 |
| Monetary and insurance coverage actions | 7.37 | 7.29 |
| Actual property actions | 8.37 | 2.17 |
| Skilled, scientific, and technical actions | 0.97 | 4.30 |
| Administrative and assist service actions | 0.72 | 5.01 |
| Public administration and protection; obligatory social safety | 8.15 | 5.30 |
| Training | 8.22 | 4.07 |
| Human well being and social work actions | 1.92 | 6.51 |
| Arts, leisure, and recreation; Different service actions | 0.59 | 5.21 |
Supply: NSO (2023)
Causes for the Present Financial Downturn
Shopper spending, which is an important measure of a wholesome financial system, is slowing down. That is partly because of inflationary pressures, which point out a weakening financial system that has dampened the market’s enthusiasm. The costs of important commodities, reminiscent of rice, lentils, dairy merchandise, edible oil, and greens, have since surged. As well as, transportation fares and gas costs have elevated. In mid-March 2023, the y-o-y client worth inflation stood at 7.44% in comparison with 7.14% a yr in the past. Whereas non-food and repair inflation elevated to eight.87%, meals, and beverage inflation remained at 5.64%. Regardless of the brand new authorities taking workplace, the financial system has been affected by a credit score crunch, a slowdown in the true property market, a falling inventory market, and rising unemployment. The liquidity crunch in Nepal’s banking sector, mixed with the central financial institution’s financial coverage geared toward controlling credit score growth, had a big impression on companies. These components resulted in hovering rates of interest, making it tough for industries to repay their money owed or encourage companies to borrow cash to develop operations. Banks had been additionally restricted in giving credit score to unproductive sectors, reminiscent of actual property and the secondary inventory market, additional affecting the move of cash available in the market.
The federal government’s poor governance and sluggish income assortment have resulted in dismal capital expenditure, which has additional lowered the circulation of cash available in the market. The import ban, which was carried out final yr to protect international trade reserves, together with the requirement of a 100% money margin for Letters of Credit score, has additionally affected consumption. Because of this, the federal government’s income assortment, which is essentially depending on import taxes, has been severely impacted. This has led to the federal government’s incapacity to pay contractors engaged on infrastructure developments, who, in flip, weren’t in a position to pay their suppliers and workers, leading to decrease demand and consumption within the financial system. Overseas direct funding additionally hit a file low, falling sharply to NPR 1.17 billion (USD 8.94 million) within the first eight months of the FY 2022/23 from NPR 16.30 billion (USD 124.61 million) throughout the identical interval of the earlier fiscal yr.
With the vast majority of Nepal’s financial sectors experiencing a slowdown, the nation is actually compelled to finance its bills by way of exterior borrowings with conditionality, which could push the nation right into a vicious cycle of borrowing extra to repay the prevailing exterior debt.
Outlook
The easing of import restrictions, the gradual reducing of rates of interest, the reducing value of inputs like gas, the relief of actual property and housing restrictions, and the optimistic outlook for tourism and the influx of remittances – all level to a potential acceleration of financial exercise within the years to return. The important thing to combating the present financial disaster will probably be enhancing home useful resource mobilization, well timed capital finances execution by the federal government, and enacting robust coverage changes to extend non-public sector confidence. Moreover, given the severity of the disaster, political stability and collaboration amongst political events on reviving the sluggish financial system, creating jobs, and liberating up public spending is extraordinarily vital.
[ad_2]
Source link


