[ad_1]
Regardless of the annual reoccurrence of the disasters, there’s an absence of complete information regarding Nepal’s historic floods and landslides, land floor attributes, vulnerability dangers, and rainfall patterns. Nepal’s Catastrophe Threat Discount Portal has information solely from 2011 of which a variety of data is lacking.
The monsoon season is the season of financial prosperity in Nepal. Yearly from June to September, the monsoon rains drench Nepal in persistent downpours with a lot of the nation experiencing 80% of its annual precipitation. This seasonal rain is essential for sustaining the agricultural sector which makes up 23.5% of the GDP. Summer season harvests similar to rice alone contributes over 11% to the GDP. The monsoon season performs a pivotal position in replenishing water assets similar to groundwater, lakes and rivers, and reservoirs. Together with sustaining Nepal’s biodiversity, they facilitate Nepal’s hydroelectric sector, which has been rising as a big contributor to Nepal’s economic system.
Determine 1: The common annual prevalence of varied pure hazards in Nepal
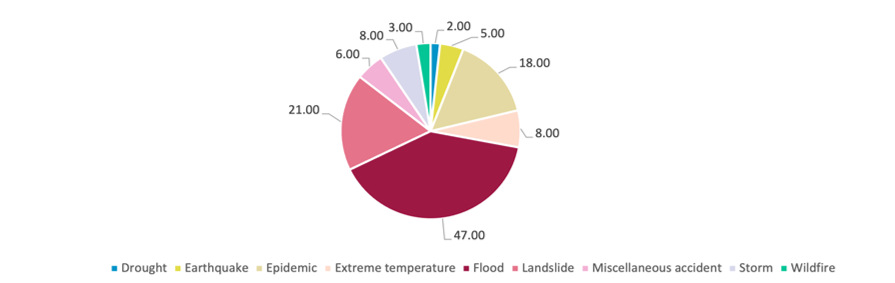
Supply: Local weather Information Portal, World Financial institution
Whereas the monsoon rains deliver hope of prosperity and life, it additionally brings foreboding of loss of life and destruction. Yearly, steady and heavy rainfall triggers landslides and floods all through the nation. It impacts impacting 1000’s of individuals by way of the lack of life, property, infrastructure, agricultural yield, and livestock. Previously few years, elevated irregularity of precipitation patterns has additional exacerbated the affect of monsoon-related pure disasters. In 2021, above-average rainfall triggered 144 floods, a big improve from the 91 floods that had been recorded in 2020. The identical yr, western Nepal noticed heavy rainfall and flooding which destroyed 1000’s of hectares of paddy crops, affecting the livelihoods and meals safety of the locals.
Why are floods and landslides catastrophic in Nepal?
Elevated vulnerability to pure disasters throughout monsoons is because of each anthropogenic and pure/environmental causes. Nepal’s naturally steep mountainous terrain and terraced hills mixed with the monsoon rains is a hotbed for landslides. Moreover, Nepal’s huge system of rivers and waterbodies makes the nation vulnerable to floods. Anthropogenic actions similar to mining, tunneling, deforestation, and unregulated building of buildings additionally improve casualty in the course of the monsoon season. Unmanaged deforestation has enormously elevated landslide danger because it reduces slope stability and will increase susceptivity to erosion. Moreover, haphazard building of buildings, particularly alongside floodplains, will increase infrastructural and social vulnerability to smaller-scale disasters. These anthropogenic elements paired with the pure topography of the nation and elevated local weather change penalties contribute to Nepal’s sensitivity to local weather danger and excessive climate occasions.
Why haven’t measures taken to restrict casualty been efficient?
Flooding and landslides had been occurring periodically yearly for many years but Nepal has not been in a position to successfully mitigate and adapt. This may be attributed to the federal government having a reactive catastrophe administration plan quite than a proactive strategy. Yearly, the federal government anticipates the monsoon season and the pure disasters, and yearly motion towards these disasters shouldn’t be taken till they’ve already occurred. Regardless of the decades-long program and mission funding by numerous growth companions, there doesn’t appear to be an environment friendly strategized plan on the native, provincial, or nationwide ranges. The inefficient response could be attributed to the lack of understanding and preparedness amongst authorities authorities and elected representatives.
A research in 2020 discovered {that a} concerningly excessive proportion of native authorities didn’t perceive the roles and duties of catastrophe danger administration and response beneath the federal system of governance (Determine 2). The shortage of basic understanding serves as a problem for native authorities to effectively perform evacuation measures, search and rescue operations, handle data, and supply mass take care of victims.
Determine 2: Native authorities’ data on questions requested about catastrophe danger administration and response in Nepal
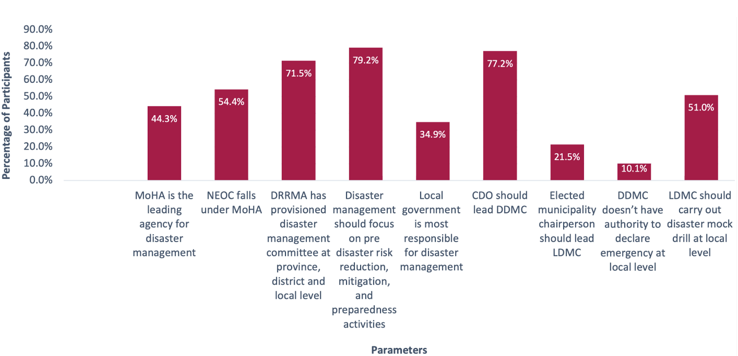
Supply: Malla, Shrijan Bahadur, Ranjan Kumar Dahal, and Shuichi Hasegawa. “Analyzing the Catastrophe Response Competency of the Native Authorities Official and the Elected Consultant in Nepal.” Geoenvironmental Disasters 7, no. 1 (2020).
The shortage of correct information is one other impediment for the federal government in taking proactive motion. Regardless of the annual reoccurrence of the disasters, there’s an absence of complete information regarding Nepal’s historic floods and landslides, land floor attributes, vulnerability dangers, and rainfall patterns. Nepal’s Catastrophe Threat Discount Portal has information solely from 2011 of which a variety of data is lacking. Within the portal, the federal government estimates “financial loss” for every pure catastrophe occasion. Nonetheless, solely a handful of those occasions have precise quantitative estimations. Additionally it is unclear what “estimated loss” entails as there is no such thing as a indication of whether or not it’s lack of property, life, or infrastructure, amongst different doable elements. This hinders the flexibility to make knowledgeable and evidence-based selections, particularly as a result of entry to such data might permit for preventative measures to cut back catastrophe impacts. Nepal’s sparse and scattered information makes it difficult to foretell excessive climate patterns and the disasters that observe them.
Manner ahead
In 2021, the federal government accredited an adaptation-based motion plan that addressed local weather vulnerabilities and dangers within the quick, medium, and long run. The Nationwide Adaptation Plan (2021-2050) set out precedence packages in 9 sectors to cut back local weather vulnerability and danger. As a part of the variation plan, the catastrophe danger discount and administration sector goals to construct local weather resilience by way of coverage reforms. It’s going to additionally keep, improve, and strengthen early warning techniques and multi-hazard monitoring to permit for local weather adaptive actions. Parallelly, the water useful resource and vitality sector goals to bridge local weather data gaps and promote climate-informed decision-making. A part of the objective for this sector is to determine a Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) danger discount and early warning techniques and assemble local weather resilient test damns.
Together with authorities efforts, ICIMOD is engaged on customizing NASA GSFC’s Landslide Hazard Evaluation for Situational Consciousness mannequin to develop a landslide mapping and forecasting system for Nepal. This landslide stock can be utilized to make data-backed selections that ought to enhance hazard administration and motion plans. The mannequin can even generate landslide predictions which may assist early warning techniques and evacuation. Equally, the establishment has an present Flash Flood Prediction Device (FFPT) for Nepal that predicts flash floods for over 12,000 river segments in Nepal. FFPT can be utilized for flood forecasting, early warning system, and response selections.
It’s crucial for the federal government to successfully combine such instruments and fashions into its catastrophe danger administration technique to cut back the harm and destruction that comes with the monsoon rains. Because the annual impacts of local weather change intensify, the federal government should prioritize funding in information assortment and evaluation in any respect ranges. By doing so, a proactive catastrophe administration system could be successfully applied earlier than it reaches some extent past our management.
[ad_2]
Source link


