[ad_1]
NASA’s James Webb House Telescope has delivered an awe-inspiring glimpse into the guts of our galaxy, revealing a mesmerizing sight of Sagittarius C (Sgr C), a star-forming area residing roughly 300 light-years away from Sagittarius A, the Milky Manner’s central supermassive black gap. On this lately captured picture, among the many ample 5,00,000 stars, a set of protostars steals the highlight. These protostars, of their embryonic part and gathering mass, emit blazing outflows that resemble a fiery show inside an infrared-dark cloud.
“There’s by no means been any infrared knowledge on this area with the extent of decision and sensitivity we get with Webb, so we’re seeing numerous options right here for the primary time,” mentioned the NASA in a launch. The remark crew’s principal investigator Samuel Crowe, an undergraduate pupil on the College of Virginia in Charlottesville, mentioned, “Webb reveals an unimaginable quantity of element, permitting us to check star formation on this type of surroundings in a approach that wasn’t doable beforehand.”
Pictured: An estimated 500,000 stars.
That is the guts of the Milky Manner galaxy. @NASAWebb has revealed never-before-seen options in a star-forming area referred to as Sagittarius C: https://t.co/ljZyx7qV2y pic.twitter.com/WgBH45qUyQ
— NASA (@NASA) November 20, 2023
“The galactic heart is probably the most excessive surroundings in our Milky Manner galaxy, the place present theories of star formation might be put to their most rigorous check,” added professor Jonathan Tan, one in every of Crowe’s advisors on the College of Virginia.
Nestled inside this youthful cluster is a identified huge protostar, surpassing 30 instances the mass of our Solar. Curiously, the density of the cloud shrouding these protostars obstructs the sunshine from stars positioned behind it, creating the phantasm of a much less populated space when, in actuality, it is one of many galaxy’s most densely packed zones. The picture showcases smaller infrared-dark clouds, resembling star-filled voids, the place forthcoming stars are taking form.
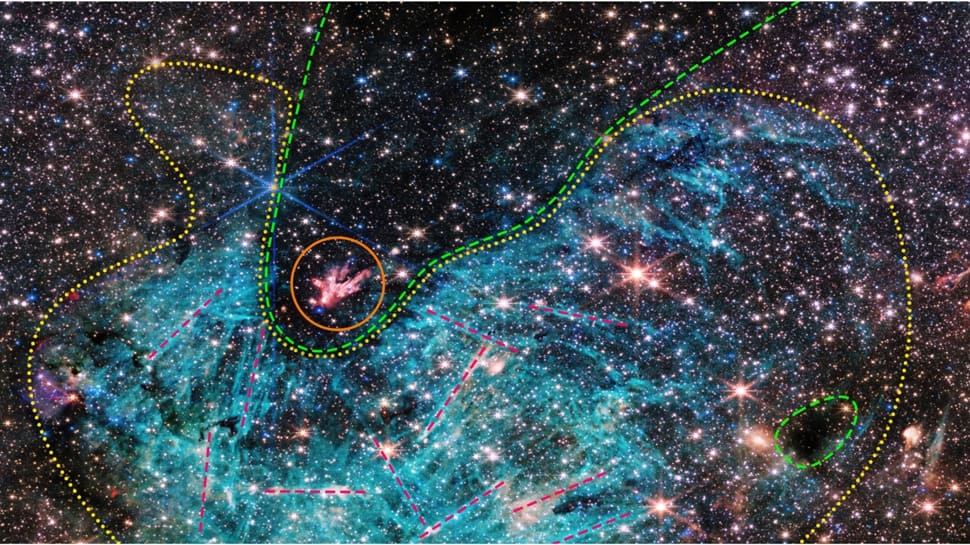
The NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digital camera) instrument of Webb’s telescope has captured in depth ionized hydrogen emissions encircling the underside of the darkish cloud, depicted in cyan hues. Often attributed to energetic photons emitted by younger huge stars, the in depth attain of this hydrogen area, a revelation dropped at gentle by Webb, poses an intriguing puzzle requiring deeper exploration. One other enigmatic function below scrutiny is the erratic needle-like constructions inside the ionized hydrogen, scattered chaotically in numerous instructions, a phenomenon demanding additional investigation by specialists.
“The galactic heart is a crowded, tumultuous place. There are turbulent, magnetized gasoline clouds which are forming stars, which then impression the encompassing gasoline with their outflowing winds, jets, and radiation,” mentioned Rubén Fedriani, a co-investigator of the mission on the Instituto Astrofísica de Andalucía in Spain.
As Webb’s revelations proceed to unfold, these gorgeous findings from the guts of our galaxy open doorways to deeper cosmic secrets and techniques, beckoning scientists to unravel the mysteries shrouded inside the celestial expanse. Round 25,000 light-years from Earth, the galactic heart is shut sufficient to check particular person stars with the Webb telescope, permitting astronomers to collect unprecedented data on how stars type, and the way this course of could depend upon the cosmic surroundings, particularly in comparison with different areas of the galaxy.
[ad_2]
Source link


