[ad_1]

Mercedes-Benz
Most automobile crashes start and finish in a number of seconds. That is loads of time to get in a tiny micro-nap whereas driving. The well-known asleep-at-the-wheel movie scene in Nationwide Lampoon’s Trip, the place Clark Griswold goes off to slumberland for 72 seconds whereas piloting the Wagon Queen Household Truckster (a paragon of automotive advantage however missing any superior driver security techniques), may be a comical take a look at this prospect. But when Clark have been in the actual world, he and his household would doubtless have been injured or killed—or they may have brought on related un-funny penalties for different motorists or pedestrians.
There’s loads of real-world information on the subject proper now. Early in 2023, the Vehicle Affiliation of America’s Basis for Site visitors Security printed a research estimating that 16–21 % of all deadly car crashes reported to police contain drowsy driving.
With the highway fatality numbers within the US hovering near 38,000 over the previous few years, which means between 6,080 and seven,980 highway deaths are linked to drowsy drivers. Additional analysis by the AAA’s Basis finds that drivers doubtless under-report drowsiness in all automobile crashes. Nodding off whereas driving is as harmful as—and probably extra harmful than—driving drunk. And whereas drunk-driving figures have decreased between 1991 and 2021, the alternative is true for drowsy driving.
Nissan
Automakers haven’t been unaware of the issue, both. As way back as 2007, producers like Volvo started providing drowsiness-detection techniques that monitored the driving force, although in a less complicated manner than what’s seen within the main techniques of as we speak. They sensed the velocities of inputs to steering, throttle, and brakes. Some even used a digicam aimed on the driver to discern if drivers have been turning into inattentive, together with drooping their head or just averting their view from the straight-ahead.
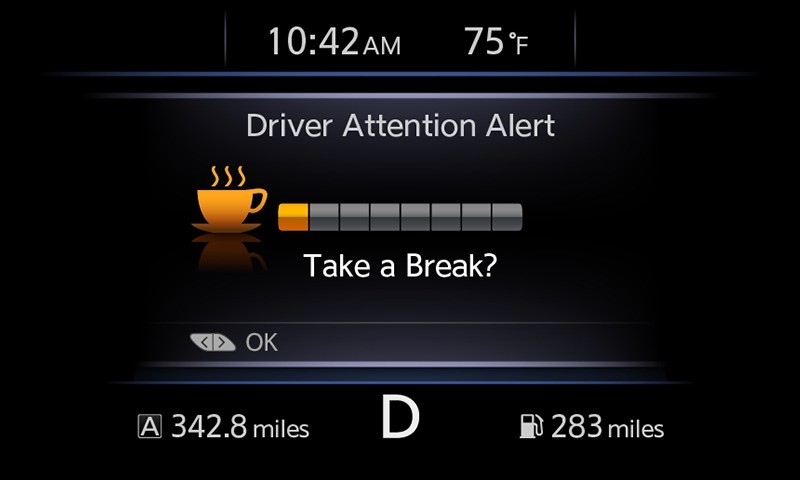
These techniques chime a warning and mission a visible alert on the dashboard asking if the driving force needs to take a break, usually with the common image for wakefulness—a espresso cup—showing within the instrument cluster. Many new automobiles as we speak nonetheless have this characteristic. And to make certain, it was then, is now, and without end might be a useful and efficient technique of alerting drivers to their drowsiness.
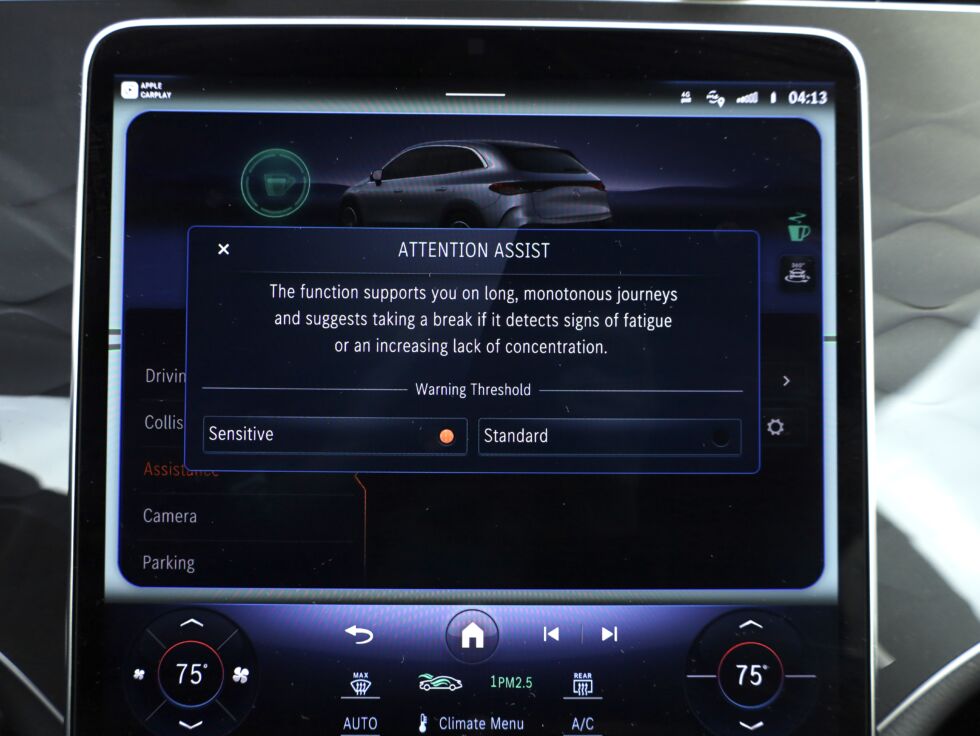
However a stage past the above audible and visible cues has modified this panorama of blunting the upward pattern of drowsy driving. As Stage-2, semi-autonomous capabilities emerge in medium- and even lower-priced vehicles, these options additionally permit automobiles and SUVs to take management of the car ought to the car decide that the driving force has grow to be inattentive or incapacitated.
Jim Resnick
As a result of all of the items of a vehicle-control puzzle are already on board, enabling a system to take over from an inattentive driver is a matter of programming—in depth programming, in fact, however all of the essential items of {hardware} are sometimes already there:
- Selective braking from adaptive cruise management and stability management
- Self-steering features of lane-keeping and lane-centering
- A mobile telematics community.
It is a prolonged programming train that may take management of a car in a simplified manner, however not earlier than three types of human stimuli are triggered to get up a drowsy driver: sight, sound, and a bodily immediate.
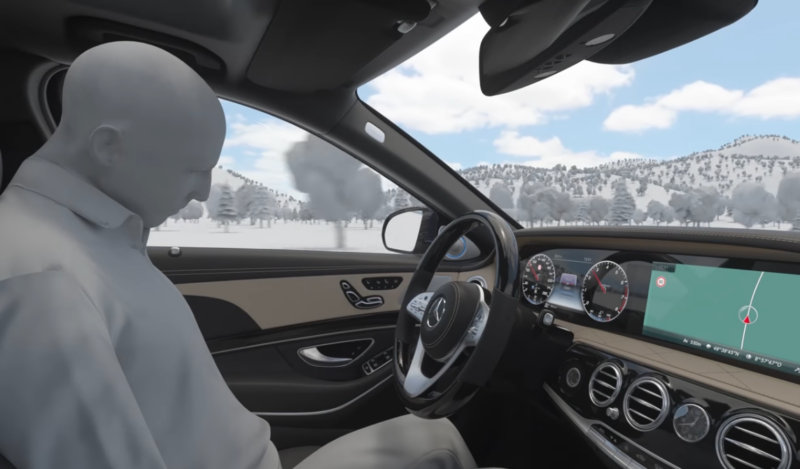
That is all nice in concept and in a digital vacuum, however I wished to discover what happens inside a automobile that has decided that the driving force is now not really driving. The Infiniti QX60 and Mercedes EQE 350 have such emergency cease capabilities; I not too long ago examined each.
[ad_2]
Source link


