[ad_1]
As in animals, crops have immune responses that assist them defend towards pathogens equivalent to viruses, micro organism, fungi, and oomycetes. Earlier than invaders might be stopped, they have to first be detected, and that is achieved by sample recognition receptors positioned on the floor of plant cells. The flexibility of those receptors to detect molecular patterns related to pathogens relies on two forms of proteins, known as RLPs and RLKs, each of which may include leucine-rich repeats—sections during which the amino acid leucine seems a number of instances.

Plant immunity receptors detect tiny pathogens like micro organism after they get inside. They’ll’t shield towards crops from being eaten.
To hint the evolution of plant immunity, the worldwide analysis workforce led by Ken Shirasu and Yasuhiro Kadota at RIKEN CSRS examined the numbers and patterns of receptors. They analyzed over 170,000 genes encoding RLKs and about 40,000 genes encoding RLPs, which they obtained from publicly accessible knowledge taken from 350 plant species. They found that RLKs and RLPs with leucine-rich repeats have been essentially the most ample receptor varieties amongst all of the plant species, making up practically half of RLKs and 70% of RLPs.
RLPs, and a few RLKs, are identified to include a particular island area that’s essential for recognizing elements of pathogens. Investigation by the RIKEN CSRS workforce revealed that amongRLPsthat include the leucine-rich repeats, this particular area was nearly all the time positioned in the identical place; between the 4th and fifth leucine-rich repeat. These RLPs have been discovered to be related to immune responses. In addition they found that the island area was positioned on the similar place in some RLKs, practically all of which belong to a practical group that regulates progress and improvement.
Comparative evaluation confirmed that the sequence of the 4 repeats under the island area was very comparable between the 2 forms of protein detectors, suggesting that they’ve a typical evolutionary ancestry. Specifically, these 4 units of leucine repeats contained sections wanted for bonding to the identical co-receptor, known as BAK1. Because of this immunity-related RLPs and growth-related RLKs inherited the power to bind BAK1 from a typical ancestor.
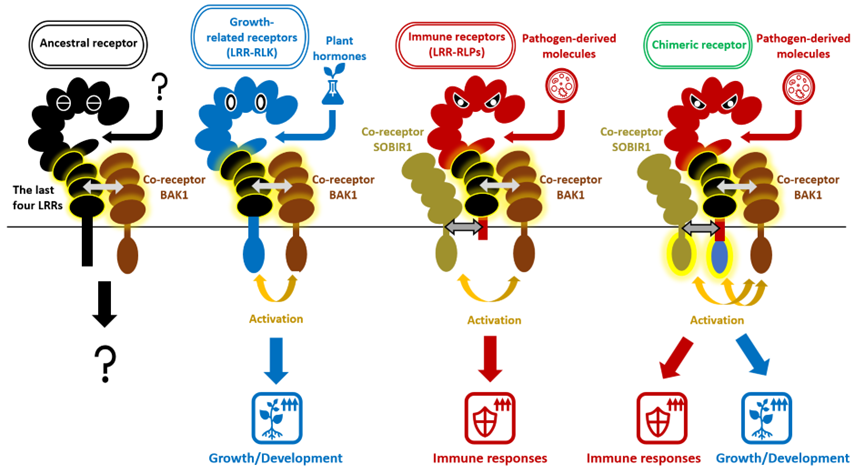
Each immunity-related LRR-RLPs and growth-related LRR-RLKs have advanced from a typical ancestor to inherit the final 4 LRRs and the power to bind the co-receptor BAK1. The chimeric receptor that includes the cytoplasmic kinase area of a growth-related LRR-RLK into an immunity-related LRR-RLP prompts each immune and progress responses upon sensing a pathogen-derived molecule. LRR, leucine-rich repeat; RLP, receptor-like protein; RLK, receptor-like kinase.
“Intriguingly, we discovered that exchanging the 4 areas of leucine-rich repeats amongst these receptors didn’t disrupt their performance,” says Bruno Pok Man Ngou, who performed the examine. Making a hybrid receptor by combining a growth-related RLK with an immunity-related RLP resulted in a hybrid receptor that acknowledged pathogens and induced each immune and growth-related responses. Because of this scientists ought to be capable of engineer receptors with new features by swapping these modules.
This examine addressed the origins of plant immunity at a molecular degree, displaying that concurrently analyzing info from a number of plant genomes can enable easy and exact prediction of genes concerned in plant immunity and progress. “We’re presently isolating immune receptors from varied crops utilizing this info, aiming for sensible purposes equivalent to creating disease-resistant crops sooner or later,” says Shirasu.
[ad_2]
Source link


