[ad_1]
China’s 31 mainland provinces, municipalities, and autonomous areas have launched their native GDP and financial indicators for 2022. The info displays the nationwide slowdown in financial development in 2022, but additionally exhibits important variations from area to area. We analyze the drivers behind the 2022 China provincial GDP figures and focus on the prospects for development in 2023.
Over the course of January, the native statistics bureaus of China’s 31 mainland provinces, municipalities, and autonomous areas (hereinafter collectively known as “provinces”) have launched native financial information for 2022. The info, which incorporates nominal GDP, GDP development charges, and typically, information on social and industrial improvement, reveals an general slowdown in financial development and social improvement from 2021 because the nation battled a number of COVID-19 outbreaks.
On the similar time, the provinces have additionally introduced their GDP development targets for 2023, which counsel widespread optimism for the 12 months forward following the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions within the fourth quarter of 2022.
Under, we analyze the native financial information for 2022 and the way the fortunes of China’s mainland provinces could change within the 12 months forward.
China provincial GDP development in 2022
Native GDP development in 2022 various enormously from province to province. The provinces with the very best annual development charges had been Fujian and Jiangxi, which grew 4.7 % from 2021 to achieve RMB 5.3 trillion (approx. US$778.1 billion) and RMB 3.2 trillion (approx. US$475.8 billion), respectively. For context, China’s complete GDP in 2022 reached RMB 121 trillion (approx. US$1.8 trillion) in 2022, a year-on-year improve of three %.
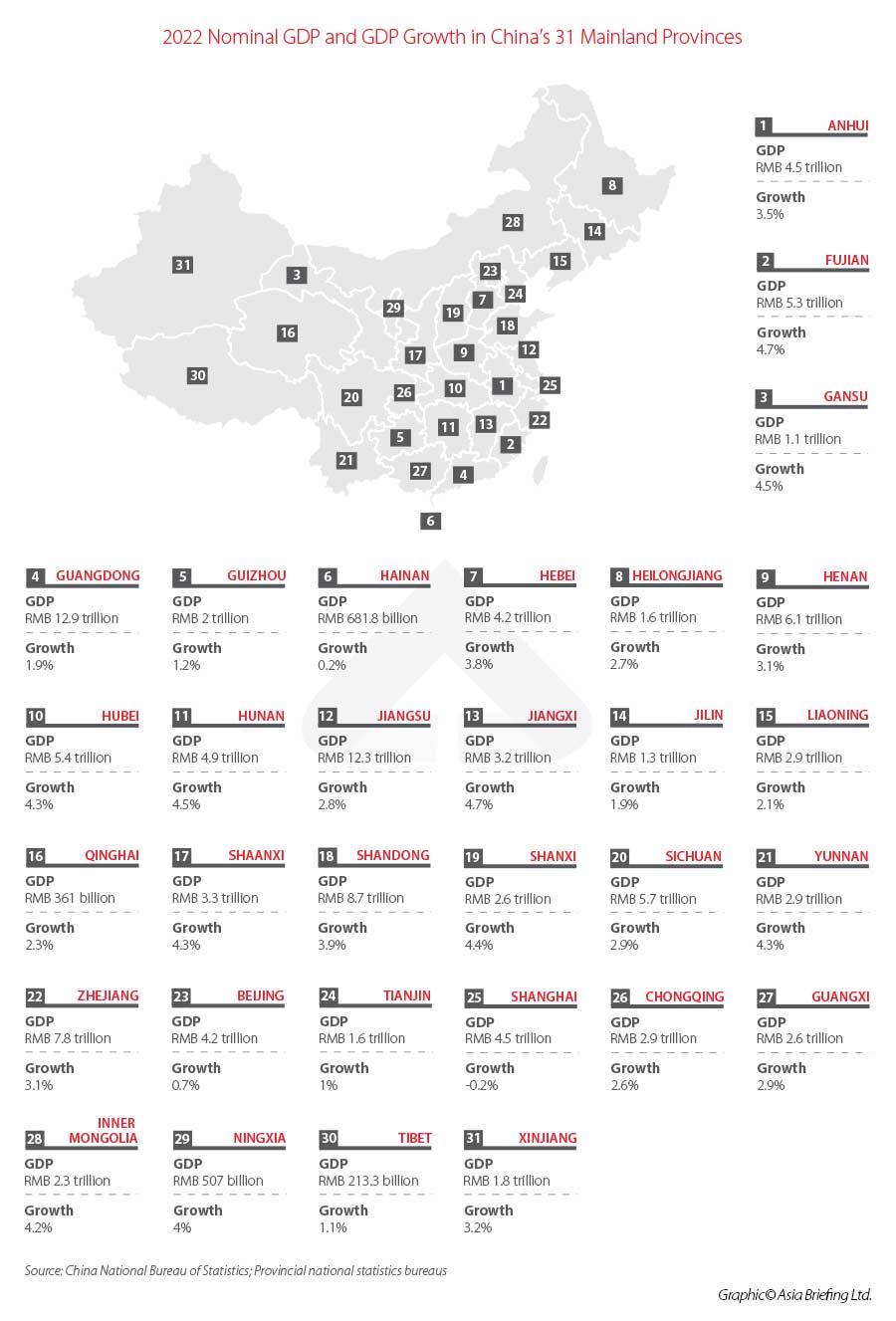
Two provinces skilled a contraction in GDP: Jilin and Shanghai. Jilin’s GDP shrank by 1.9 % year-on-year, whereas Shanghai’s shrank by 0.2 % year-on-year.
Each Shanghai and Jilin had been a number of the hardest-hit areas by the coronavirus pandemic. Jilin Province was below a strict weeks-long lockdown in March 2022, which considerably impacted the province’s manufacturing output, certainly one of its key industries. Shanghai, in the meantime, was below a two-month lockdown in April and Might, which put town at a digital standstill.
Nonetheless, each areas skilled a restoration within the latter half of the 12 months. Shanghai’s GDP contracted at a fee of 5.7 % within the first half of 2022 however narrowed to -1.4 % within the first three quarters. Jilin, in the meantime, skilled a contraction of seven.9 % within the first quarter, which had narrowed to -1.6 % by the top of the third quarter.
Guangdong Province remained the biggest province in China by nominal GDP, reaching RMB 12.9 trillion (approx. US$1.9 trillion), up 1.9 % year-on-year. This was adopted by Jiangsu, which reached RMB 12.3 trillion, up 2.8 % year-on-year.
The provinces with the bottom nominal GDP had been Tibet (RMB 213.3 billion; approx. US$31.7 billion) adopted by Qinghai (RMB 361 billion; approx. US$53.7 billion).
No province exceeded the 2022 nationwide GDP development goal of “round 5.5 %”.
Regardless of its contraction, Shanghai remained the only largest metropolis in China by GDP in 2022. This was adopted by Beijing, with a neighborhood GDP of RMB 4.2 trillion (US$624.5 billion), and Shenzhen, which reached RMB 3.2 trillion (approx. US$475.8 billion).
In the meantime, Chongqing overtook Guangzhou to turn into the fourth-largest metropolis in China by GDP. Chongqing’s complete GDP in 2022 was RMB 2.91 trillion (approx. US$432.7 billion), whereas Guangzhou’s fell simply wanting that at RMB 2.88 trillion (approx. US$428.3 billion).
Business output and retail gross sales in 2022
Industrial value-add to the financial system various enormously from province to province in 2022, suggesting the various levels to which the COVID-19 pandemic impacted totally different areas.
The western province of Qinghai punched above its weight with the very best development in industrial value-add of firms above the designated measurement (these with a most important enterprise revenue of above RMB 20 million or roughly US$3 million), accelerating 15.5 % year-on-year. In the meantime, the worst-performing area was Beijing, whose industrial value-add dipped by 16.7 % year-on-year.
The nationwide common development fee of business value-add in 2022 was 3.6 % year-on-year.
Qinghai’s industrial exercise was buoyed by sturdy development in sectors reminiscent of its salt lake chemical substances trade (up 31.3 % year-on-year), together with lithium carbonate (24.5 %), potash fertilizer (13.3 %), and uncooked salt (24.3 %), in line with information from the Qinghai Provincial Bureau of Statistics.
In Beijing, the steep contraction reversed when accounting for the impression of the manufacturing of the coronavirus vaccine. Beijing is dwelling to main vaccine manufacturing services – reminiscent of that of the pharmaceutical big Sinovac – and demand for vaccines in 2022 dropped considerably as most individuals had already accomplished their two rounds of inoculation in 2021.
As well as, excessive base results from 2021 dragged considerably on the 2022 determine. In 2021, due to main vaccine drives in each China and abroad, the value-add of Beijing’s pharmaceutical manufacturing trade grew by a staggering 252.1 % year-on-year, accounting for round 30 % of the entire trade value-add of firms above a delegated measurement that 12 months.
Damaged down by trade, we will see that the pharmaceutical manufacturing trade dragged on general development in 2022 with a contraction of 58.3 %. Nonetheless, when eradicating elements related to the manufacturing of coronavirus vaccines, the economic value-add of the pharmaceutical manufacturing trade grew by 6.4 %, and general industrial value-add grew by 2.5 %.
A number of different industries noticed optimistic development in 2022, together with gear manufacturing (10.2 %), railway, ship, aerospace, and different transportation gear manufacturing (3.7 %), and manufacturing of devices and equipment (2.5 %).
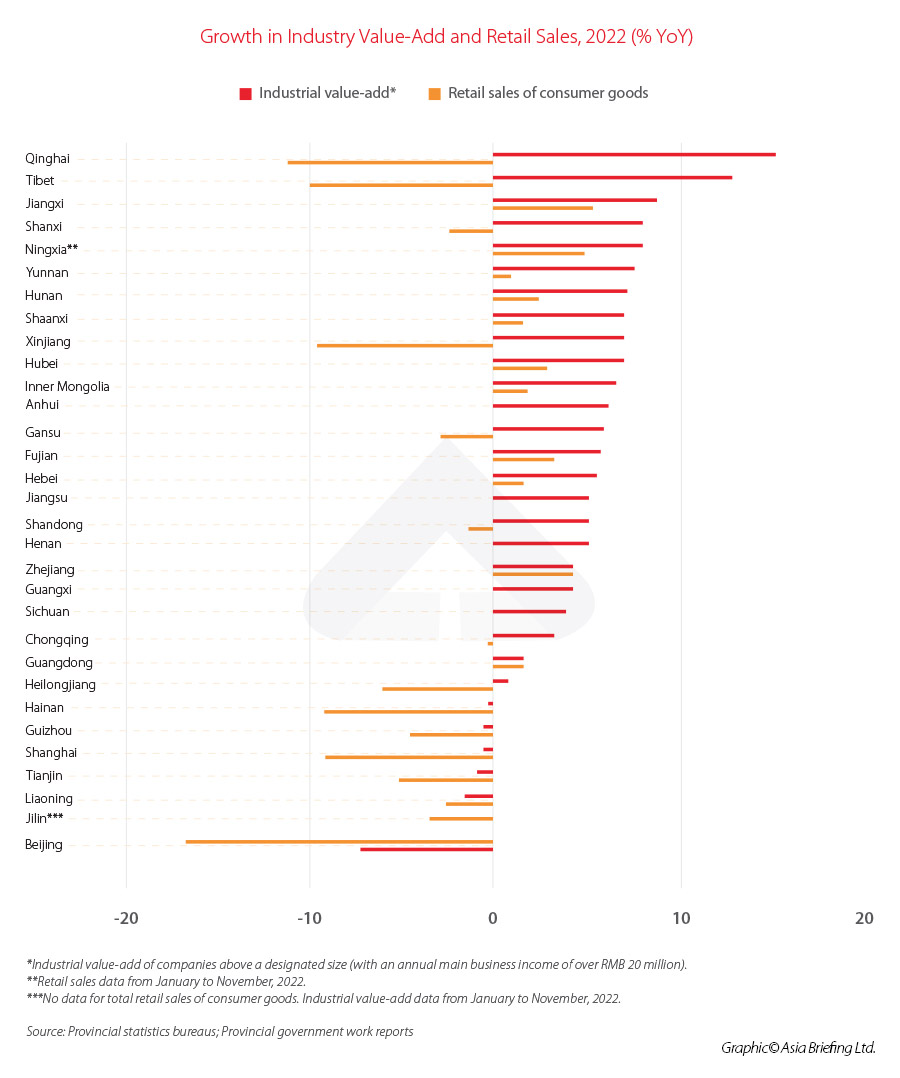
Retail gross sales of client items on common fell by 0.2 % year-on-year in 2022 throughout the nation, with virtually half of provinces experiencing a contraction.
The provinces with the steepest year-on-year fall had been Qinghai (-11.2 %) and Tibet (-10 %). Main cities, reminiscent of Beijing and Shanghai, additionally noticed steep declines (-7.2 and -9 % respectively) as COVID-19 restrictions slowed financial exercise and consumption.
Nonetheless, provinces reminiscent of Jiangxi and Ningxia fared comparatively effectively, with retail gross sales rising 5.3 % and 5 %, respectively. These provinces skilled fewer disruptions from COVID-19 outbreaks in comparison with different areas and usually carried out effectively throughout all most important financial indicators.
China provincial GDP prospects for 2023
China’s mainland provinces have additionally launched their GDP development targets for 2023. These targets are virtually all very bold, suggesting widespread optimism concerning the financial system within the coming 12 months.
This optimism is largely spurred by the central authorities’s resolution to abolish its zero-COVID coverage in late 2022, which noticed the lifting of nearly all of the restrictions that had hampered development in recent times. Furthermore, the central authorities additionally set a daring new pro-growth financial agenda for 2023.
Presently the central authorities has not but set an official nationwide GDP development goal for 2023. Historically, it’s introduced through the Two Periods conferences held yearly at first of March. Nonetheless, the central authorities is just not required to set a concrete GDP development goal, and it’s not sure whether or not it’ll accomplish that this 12 months. In the meantime, the Worldwide Financial Fund (IMF) has upwardly revised its forecast for China’s GDP development in 2023 to five.2 % from its earlier projection of 4.4 %.
The vast majority of provinces have set their native GDP targets for 2023 at above 5 % year-on-year. The notable exceptions are Beijing and Tianjin, which have set their development targets at “above 4.5 %” and “round 4 %”, respectively.
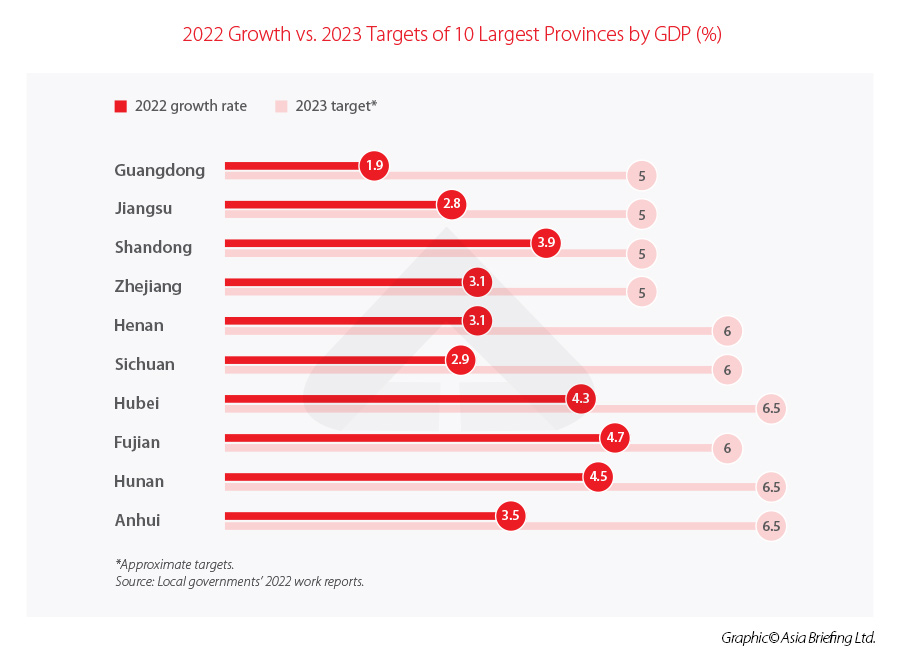
The very best development goal of any province was set by Hainan, which is aiming to realize “round 9.5 %” year-on-year development in 2023. That is notably bold given Hainan’s annual GDP development fee in 2022 was simply 0.2 % year-on-year.
The island province was hit laborious by the pandemic not due to native outbreaks however relatively attributable to its heavy reliance on tourism, which took a pointy dive on account of the COVID-19 journey restrictions. Nonetheless, its financial exercise recovered within the second half of the 12 months, going from a 2.5 % contraction within the second quarter and recovering to 1.9 % year-on-year development within the fourth quarter.
With the elimination of COVID restrictions, journey and tourism are anticipated to rebound, which is able to assist to spur financial development. The creation of a free commerce port on the island, in addition to the introduction of assorted preferential insurance policies, can also be hoped to spice up enterprise exercise.
Hainan is likely one of the provinces with important development potential as it’s nonetheless underdeveloped in comparison with its counterparts in japanese and southern China. Its GDP per capita, at RMB 66,845 (approx. US$9,940), remains to be beneath the nationwide common of RMB 85,698 (approx. US$12,743).
Typically, the provinces with probably the most bold development targets – Tibet (round 8 %), Xinjiang (round 7 %), and Jiangxi (round 7 %) – are all traditionally underdeveloped areas, and due to this fact have excessive development potential. The federal government has additionally been closely selling buyers and industries to maneuver to underdeveloped areas in central and western China, in an effort to steadiness financial improvement.
In the meantime, massive developed cities reminiscent of Beijing (above 4.5 %), Tianjin (round 4 %), and Shanghai (above 5.5 %), have set barely extra modest targets.
Additionally it is price declaring that, as a result of low development charges recorded in 2022, base results will assist to spice up the 2023 financial indicators. Which means that many provinces have an excellent probability of recording sturdy GDP, trade, and consumption development charges, particularly within the second and third quarters when many of the nation skilled a major slowdown in financial exercise.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The observe assists overseas buyers into China and has achieved so since 1992 via places of work in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the agency for help in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has places of work in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, along with our commerce analysis services alongside the Belt & Street Initiative. We even have associate corporations aiding overseas buyers in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
[ad_2]
Source link


