[ad_1]
Within the realm of Fintech, whereas rising economies like Nepal have made strides in adopting applied sciences like cost gateways, cashless funds, and on-line banking, the worldwide panorama of economic know-how encompasses a various vary of improvements. These span the mixing of banking information with third-party monetary companies, the applying of Synthetic Intelligence and large information analytics to discern client conduct patterns for credit score threat evaluation and enhanced companies.
The time period “Fintech,” an abbreviation for Monetary Expertise, initially referred to the technological techniques that strengthened the operations of economic establishments like banks and company entities. Nevertheless, this definition has developed considerably in latest occasions, now encompassing a broader spectrum of financial sectors that leverage technological developments to boost the effectivity of economic establishments. Nepal’s journey in the direction of integrating know-how into its monetary sectors started with NABIL Financial institution (previously generally known as Nepal Arab Financial institution) introducing bank cards in 1990. Regardless of the speedy penetration of simple web entry and smartphones within the Nepali market, the adoption of digital cost applied sciences remained comparatively sluggish till the mid-2010s. The outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst, spurring each demand for and adaptation to applied sciences comparable to cell banking, QR funds, and cashless transactions. This marked the inception of the Fintech revolution in Nepal, pushed by the swift actions of banks to combine cell banking companies, Fee Service Suppliers (PSPs), and Fee Service Operators (PSOs), alongside the growing pattern of e-commerce within the nation.
Fintech: World and Nepali State of affairs
Within the realm of Fintech, whereas rising economies like Nepal have made strides in adopting applied sciences like cost gateways, cashless funds, and on-line banking, the worldwide panorama of economic know-how encompasses a various vary of improvements. These span the mixing of banking information with third-party monetary companies, the applying of Synthetic Intelligence and large information analytics to discern client conduct patterns for credit score threat evaluation and enhanced companies, and the usage of blockchain for safe transactions and settlement validation.
The Nepal Monetary Inclusion Report 2023 by the IFC reveals a considerable progress within the adoption of fintech amongst Nepali customers. Over eight years, cell banking customers grew at a formidable Compound Annual Progress Fee of 58.14%, reaching 18.31 million customers, or 62.8% of the inhabitants in mid-July 2022. QR-based funds additionally skilled a surge, with transaction quantity growing from Rs. 7.76 billion in 2022 to Rs. 20.77 billion in mid-March of 2023. Notably, authorities income assortment has seen a digital shift, with 30% attributed to digital funds and 90% of transactions executed digitally. The widespread adoption of Fee Service Suppliers (PSPs) purposes, downloaded by over 10 million customers, has facilitated utility funds, purchases, subscriptions, and extra. These apps allow seamless cash transfers and have boosted ecommerce and service provider funds. Industrial banks like NIC ASIA and Machhapuchhre have launched progressive voice-based QR funds, benefiting visually impaired customers.
Whereas Nepal’s fintech adoption is spectacular, the NRB’s Monetary Entry report from mid-June 2020 highlights that solely 67.3% of the inhabitants held a checking account. Conventional strategies like cheques and money deposits proceed to deal with a good portion of transactions, indicating areas for additional improvement.
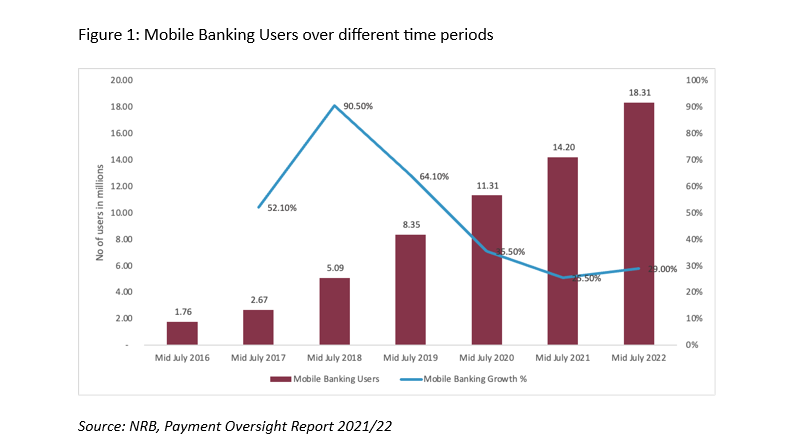
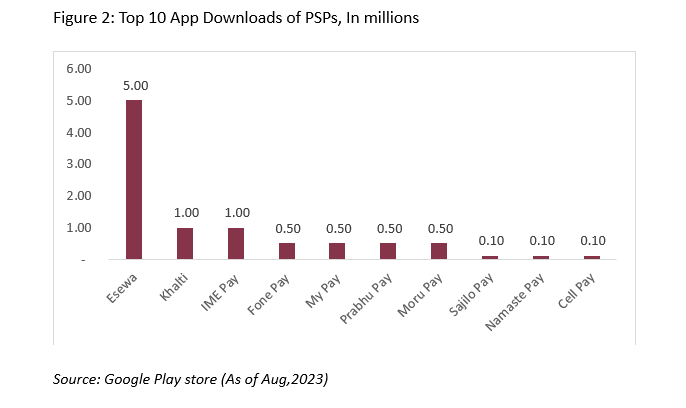
Key Gamers Shaping Nepal’s Fintech Panorama
A number of key stakeholders have performed pivotal roles in propelling Nepal’s Fintech revolution:
- Authorities Entities: Nepal Rastra Financial institution, because the central banking authority, has been instrumental in fostering the brand new laws and pointers for FinTech business to develop in Nepal. The Fee and Settlement Act launched by NRB in 2019 offered the authorized foundation for the event, enlargement, promotion, monitoring, and regulation of the funds, settlement, and clearing techniques in Nepal.
- Company Banks: The vast majority of business and company banks in Nepal promptly responded to the demand for digital banking, providing clients user-friendly cell banking options together with cell recharge and invoice funds.
- Fee Service Operators (PSOs): At the moment, Nepal boasts 10 registered PSOs, with Fonepay and ConnectIPS rising as extremely fashionable selections. Fonepay, developed by F1Soft Applied sciences, integrates with quite a few banks to supply digital banking networks and transaction settlements. Equally, ConnectIPS, launched by Nepal Clearing Home Restricted, empowers banks to independently confirm client accounts and hyperlink them to the applying portal for seamless inter-banking and cost companies.
- Fee Service Suppliers (PSPs): Nepal at the moment homes 27 registered PSPs. In the meantime business banks, improvement banks, and finance corporations have obtained licenses to function as PSPs. Whereas PSOs like Fonepay and SmartQR facilitate most cell banking purposes, PSPs like Khalti, eSewa, and ImePay have gained prominence with their digital pockets purposes. These platforms empower customers to conduct banking transactions, digital funds, invoice funds, e-commerce transactions, and extra via a unified utility.
- FinTech Alliance Nepal: Recognizing the importance of the Fintech revolution, key gamers in Nepal’s market have established the FinTech Alliance. This entity actively expands its community to attach company traders, together with personal fairness and enterprise capital corporations, with Fintech giants and startups in Nepal, fostering the trade of progressive concepts and improvement inside this area.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Regardless of Nepal’s strides in integrating know-how into its monetary panorama, quite a few challenges should be addressed to realize world Fintech inclusion. The Nepali authorities has deemed blockchain know-how and cryptocurrency unlawful, citing issues over escalating outward remittances and high-risk transactions. This stance contrasts with worldwide banking sectors which are embracing blockchain applied sciences to optimize cross-border funds, streamline commerce finance via good contracts, and revolutionize typical banking practices via safe and decentralized frameworks. Moreover, Nepal faces a shortage of expert human sources to develop Fintech applied sciences. Whereas Nepal’s IT service business is prospering, many IT graduates and consultants search alternatives overseas. Even these working inside Nepal are likely to go for freelancing contracts with international businesses or predominantly interact with corporations outsourcing work from Western international locations. To drive Fintech innovation, stakeholders want to acknowledge the potential of Nepali IT consultants and leverage these sources to drive technological development throughout the Fintech sector.
As we talk about additional in regards to the challenges of FinTech progress in Nepal, it is usually necessary to handle the truth that a major inhabitants of Nepal lack monetary literacy. A survey performed by NRB in 2022 stories the mixture nationwide monetary literacy to be simply at 57.9%. The exponential progress of know-how poses dangers comparable to id theft and on-line scams in the direction of such inhabitants group. Compared with different international locations, Nepal is in dire must speed up concerted marketing campaign aimed toward enhancing consciousness concerning each banking and non-banking institutions.
NRB revealed an idea report in 2022 concerning Central financial institution digital foreign money. That is an effort by NRB to analysis on implementing digital foreign money as already initiated and carried out by many different international locations. Its intention is to ascertain coverage objectives in bettering funds entry, selling monetary inclusion, safeguarding the central financial institution’s financial sovereignty, enhancing the effectivity of the cross-border cost techniques, selling monetary transparency and bettering financial coverage transmission mechanism. Likewise, NCHL additionally just lately signed a MoU with Indian cost techniques to allow cross border cost eradicating a major barrier that Nepal has with international cost gateways. Additionally, with rising recognition of Open banking in world area, NCHL can also be implementing Nationwide Fee Interface (NPIs) which permits a number of monetary organizations to share transaction and banking particulars via API (Software Program Interface) calls with out having to carry out any bodily visits to those establishments.
Conclusion
In abstract, Fintech holds promising prospects in Nepal, with authorities and personal entities tirelessly striving to handle native calls for and open new avenues on this area. The rising demand for digital options amongst Nepali society has considerably propelled the inclusion of Monetary Expertise. Nonetheless, Nepal wants to handle challenges obstructing Fintech’s progress and sustainability. This includes independently selling and implementing Fintech corporations and their purposes(companies). This step will advance Nepal’s technological adaptation according to world context, fostering monetary inclusion and the digital financial system.
[ad_2]
Source link


